|
CT Detects Early Lung Cancer | More Good Mammo AI News
September 11, 2023
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“CT’s are pretty fast, but there’s a lot of opportunity on the steps before and after to really speed that workflow and really improve operational efficiency.”
|
|
J Anders of GE HealthCare, in a new Imaging Wire Show about CT efficiency.
|
|
|
CT is medical imaging’s workhorse modality, but there is still room for improvement when it comes to driving efficiency and better patient care. In this episode of The Imaging Wire Show, we talked to Dr. David Furman of St. Luke’s University Health Network and J Anders of GE HealthCare on recent developments to make CT even better.
|
|
|
|
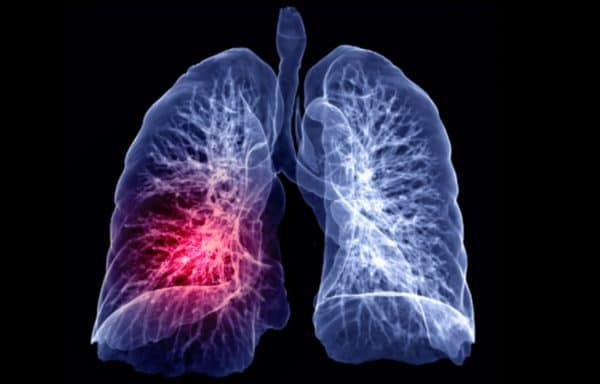
A massive CT lung cancer screening program launched in Taiwan has been effective in detecting early lung cancer. Research presented at this week’s World Conference on Lung Cancer (WCLC) in Singapore offers more support for lung screening, which has seen the lowest uptake of the major population-based screening programs.
Previous randomized clinical trials like the National Lung Screening Trial and the NELSON study have shown that LDCT lung cancer screening can reduce lung cancer mortality by at least 20%. But screening adherence rates remain low, ranging from the upper single digits to as high as 21% in a recent US study.
Meanwhile, lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer death worldwide. To reduce this burden, Taiwan in July 2022 launched the Lung Cancer Early Detection Program, which offers biennial screening nationwide to people at high risk of lung cancer.
The Taiwan program differs from screening programs in the US and South Korea by including family history of lung cancer in the eligibility criteria, rather than just focusing on people who smoke.
Researchers at WCLC 2023 presented the first preliminary results from the program, covering almost 50k individuals screened from July 2022 to June 2023; 29k had a family history of lung cancer and 19k were people who smoked heavily. Researchers found …
- 4.4k individuals receive a positive screening result for a positive rate of 9.2%
- 531 people were diagnosed with lung cancer for a detection rate of 1.1%
- 85% of cancers were diagnosed at an early stage, either stage 0 or stage 1
This last finding is perhaps the most significant, as part of the reason for lung cancer’s high mortality rate is that it’s often discovered at a late stage, when it’s far more difficult to treat. As such, lung cancer’s five-year survival rate is about 25% – far lower than breast cancer at 91%.
The Takeaway
Taiwan is setting an example to other countries for how to conduct a nationwide LDCT lung cancer screening program, even as some critics take aim at population-based screening. Taiwan’s approach is broader and more proactive than that of the US, for example, which has erected screening barriers like shared decision-making.
Although it’s still early days for the Taiwan program, future results will be examined closely to determine screening’s impact on lung cancer mortality – and respond to screening’s critics.
|




|
|
How Thomas Jefferson Leveraged CARPL.ai
See how Thomas Jefferson University relied on CARPL.ai to accelerate its AI validation and clinical adoption in this presentation by informatics and AI leader, Dr. Paras Lakhani.
|
|
Solutions to Transform Medical Image Delivery
Medical providers and health systems are looking to ditch the disc and modernize their patients’ journey. Learn how Clearpath helps them reduce the cost of retrieving and fulfilling patient requests for imaging and medical records.
|
|
- Reducing Smoking’s Stigma: In another study from WCLC 2023, people who smoke and then develop lung cancer face social stigma that can lead to worse psychosocial outcomes. In a review of 10 studies, researchers found that interventions such as group programs or psychotherapy could reduce stigma. Some researchers believe that smoking-related stigma produces internalized self-blame or shame; this could reduce adherence to smoking cessation or CT lung screening attendance.
- Lung Screening Stage Shift: While we’re discussing CT lung screening, researchers in Chest described their findings in a study of 1.1M people in the ACR’s Lung Cancer Screening Registry. Screening LDCT scans were administered from 2015 to 2019, with a cancer detection rate of 0.56% on baseline scans. Like the Taiwan study, researchers saw a stage shift to stage 1 cancer from baseline to annual follow-up (40% vs. 60%). But only 22% returned for annual screening, reducing the cancer detection rate.
- More Good News for Mammo AI: Hot on the heels of the MASAI and PERFORMS studies, another clinical trial has good news for mammography AI as researchers from Sweden’s Karolinska Institutet reported results from the ScreenTrustCAD study in The Lancet Digital Health. In all, 55.5k women were screened from April 2021 to June 2022. A protocol of one radiologist working with Lunit’s INSIGHT MMG AI algorithm detected 4% more cancers than two radiologists, while cutting reading time in half and reducing false positives by 6%. Time to say goodbye to double-reading?
- Shortage of Breast Radiologists: Meanwhile, patients in northern Arizona are experiencing gaps in breast healthcare due to a shortage of breast radiologists at a radiology group that serves Verde Valley Medical Center, a community hospital two hours north of Phoenix. Part of the issue is the scarcity of radiologists with breast fellowship training, and the radiology group has seen high turnover of the breast radiologists it has hired. The situation could illustrate the need for AI to supplement humans for breast interpretation, as supported in several recent clinical trials.
- Breast Density Confusion: Women’s health advocates rejoiced when the FDA announced it was creating a national requirement to report breast density to women when they get mammograms. But the new rule could create confusion, as referring clinicians and patients would receive different information from breast imaging facilities. So says an article in JAMA Health Forum that fortunately proposes solutions: 1) targeting notifications to high-risk women, 2) using shared decision-making tools, and 3) adjusting reimbursement models to incentivize supplemental screening mostly for high-risk women.
- VHA Awards NextGen PACS Contracts: The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has awarded contracts through its National Teleradiology Program (NTP) to several imaging vendors for upgrading its PACS. NTP is the VA’s in-house teleradiology service, and the NextGen PACS project is designed to upgrade its digital image management network. Mach7 Technologies was chosen to provide VNA and diagnostic viewer software, Blackford Analysis will provide the AI platform, Nuance will supply voice recognition and radiology workflow, and Microsoft will provide its Azure cloud storage platform.
- United Installs New PET/CT: United Imaging has made the first US installation of uMI Panorama, a new PET/CT scanner the company launched at SNMMI 2023. The milestone installation took place at the Center for Quantitative Cancer Imaging (CQCI) at Huntsman Cancer Institute, part of the University of Utah healthcare system. uMI Panorama sports 2.9mm NEMA resolution, a 35cm axial field of view, and 194ps timing resolution. Huntsman last year installed two other United PET/CT scanners.
- FAPI-PET Changes Management: PET/CT imaging with 68Ga-FAPI changed patient management in over half of cancer patients in a new study in JNM. In 226 patients with various cancers scanned from 2017 to 2022, researchers compared four variants of FAPI-PET radiotracers to gold standard imaging, which ranged from CT to MRI to PET depending on cancer type. FAPI-PET changed both clinical management and TNM stage (52% and 42%), with a major change in management in 12% of patients. The findings confirm other recent studies on FAPI-PET’s utility.
- Philips Boosts CEUS Resolution: Philips has introduced a new contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) application for its Epiq Elite scanner that boosts resolution by 200%. The company’s super-resolution microvascular imaging (MVI) technology leverages contrast microbubbles as targets for localization and tracking to pinpoint microvessels; it is particularly suited for imaging blood flow dynamics to determine pathology, such as of a suspected lesion. Philips introduced MVI at last week’s International Bubble Conference in Chicago, where a talk was presented on its use for liver imaging.
- Radiation in Kids with Down Syndrome: Children with Down syndrome receive more ionizing radiation from medical imaging than other kids. In PLOS One, researchers noted that Down syndrome children receive more imaging exams due to co-morbid conditions like CNS, heart, and musculoskeletal abnormalities. They tracked radiation exposure to 3.1k children with the syndrome from a population of 4.3M, finding 9.5X the rate of ionizing radiation exposure to age 1 and 2.3X from 1-18. Clinicians should focus on reducing radiation exposure in these children.
- Lung Imaging Alliance: Polarean Imaging and VIDA Diagnostics have partnered to promote the use of hyperpolarized xenon-129 MRI for clinical and research use in lung disease. The companies will integrate Polarean’s Xenoview inhaled lung ventilation contrast agent with VIDA’s image management platform, which is in use at 1k clinical and research sites worldwide. The goal is to establish a clinical trial network for pharma-sponsored drug and device development using xenon-129. CMS in August set up an HCPCS reimbursement code, C9791, for xenon-129 imaging.
|
|
Unleash the Power of the Cloud
Change Healthcare’s cloud-native, zero-footprint Stratus Imaging PACS is live in clinical use. See how Stratus Imaging PACS is helping radiology practices improve productivity and patient care, while eliminating the cost and resource constraints of on-premise systems.
|
|
All-In with United Imaging
United Imaging’s “all-in” approach means that every system ships with its entire suite of features and capabilities (no options), giving its clients more clinical flexibility and predictability.
|
|
- Check out this Blackford Analysis video detailing how its AI platform streamlines AI adoption and workflows, allowing radiology teams to achieve AI’s clinical benefits without operational sacrifices.
- Subtle Medical and its clinical partners earned a number of spots on the semifinalist list in this year’s Minnies awards, including company founder Greg Zaharchuk, MD, PhD, as well as research partners Suzie Bash, MD; Lawrence Tanenbaum, MD; and Max Wintermark, MD. Hear them discuss SubtleSYNTH in this upcoming webinar.
- In cardiology, two prominent IT systems, CPACS and CVIS, have emerged as pivotal tools for managing the vast array of cardiology-related data. Learn the key differences between them in this Intelerad article.
- Radiology thought leaders discussed AI’s return on investment in a session from SIIM 2023. We covered some of the high points in this interview with Matt Lungren, MD, and Sander Kloet of Nuance Communications.
- Imaging AI’s clinical and productivity benefits are becoming increasingly clear, but selecting and implementing the right solution can be difficult. This Arterys paper details how an AI platform strategy allows providers to efficiently and accurately evaluate AI applications, so they can start realizing their targeted AI benefits.
- CloudPACS has finally arrived. Learn more about the benefits that cloud-based PACS can have for your radiology practice and how Visage Imaging’s Visage 7 was built from the ground up to ensure maximum performance, security, and scale.
- AI is helping improve clinical decisions and patient outcomes in Southeast Asia. Learn more in this case study how solutions from Annalise.ai are empowering clinicians to make faster and more accurate decisions.
- What’s the latest news from Merge by Merative? Get an update on the company’s activities in enterprise imaging, VNA and viewers, workflow orchestration, and radiology departmental solutions from General Manager Ashish Sant in this interview from SIIM 2023.
- Do you see room for efficiency improvement in your radiology department? Find out how you can leverage advanced technology like Enlitic’s Curie|ENDEX solution to make sure your radiologists are reporting efficiently.
- EHRs are becoming a source of frustration for physicians, and the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this trend. Learn how PocketHealth can give patients control and ownership of their records, reducing the burden on clinicians.
- The number of patients eligible for low-dose CT lung cancer screening has expanded, and so has the need to reach at-risk patients closer to where they live. That’s why Siemens Healthineers’ Mobile Lung Screening Solution combines the quality, ease of use, and flexibility needed to create a program that meets the real-life needs of your community.
- Lung cancer causes more deaths globally than colon, breast, and colon cancer combined. But technologies like AI and low-dose CT screening can help. Learn more in this Q&A with Ankur Sharma, MD, head medical affairs digital radiology at Bayer.
- New results from the OPERA study show how Us2.ai’s echo AI solution improved heart failure screening in the NHS, reducing echo waiting times from 12 months to under 6 weeks. Find out more in this article.
- Increasing demand for healthcare has led to a boom in imaging exam volume, with studies such as CT requiring complex scanning protocols. Learn how GE HealthCare is evolving CT workflows with its efficient scanning solutions.
|
|
|
Share The Imaging Wire
|
|
Spread the news & help us grow ⚡
|
|
Refer colleagues with your unique link and earn rewards.
|

|
|
|
|
Or copy and share your custom referral link: *|SHAREURL|*
|
|
You currently have *|REFERRALS|* referrals.
|
|
|
|
|