|
AI’s Physician Influence | HCC MRI Paradigm Shift
February 2, 2023
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“It is very interesting that, completely by coincidence and unrelated to my personal biases, all radiologists who read faster than me are missing too many findings and all radiologists who read slower than me are not working efficiently enough.”
|
|
A tweet from “just right” radiologist, Alex D. Bibbey, MD.
|
|
|
|
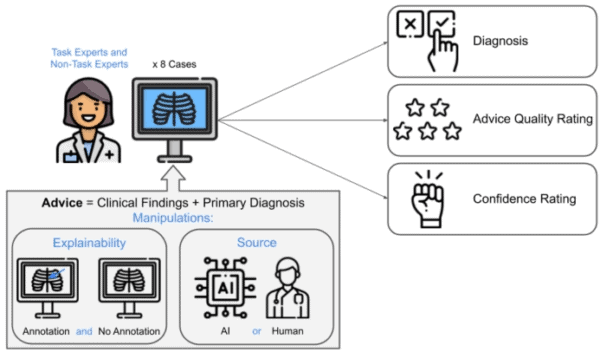
We spend a lot of time exploring the technical aspects of imaging AI performance, but little is known about how physicians are actually influenced by the AI findings they receive. A new Scientific Reports study addresses that knowledge gap, perhaps more directly than any other research to date.
The researchers provided 233 radiologists (experts) and internal and emergency medicine physicians (non-experts) with eight chest X-ray cases each. The CXR cases featured correct diagnostic advice, but were manipulated to show different advice sources (generated by AI vs. by expert rads) and different levels of advice explanations (only advice vs. advice w/ visual annotated explanations). Here’s what they found…
- Explanations Improve Accuracy – When the diagnostic advice included annotated explanations, both the IM/EM physicians and radiologists’ accuracy improved (+5.66% & +3.41%).
- Non-Rads with Explainable Advice Rival Rads – Although the IM/EM physicians performed far worse than rads when given advice without explanations, they were “on par with” radiologists when their advice included explainable annotations (see Fig 3).
- Explanations Help Radiologists with Tough Cases – Radiologists gained “limited benefit” from advice explanations with most of the X-ray cases, but the explanations significantly improved their performance with the single most difficult case.
- Presumed AI Use Improves Accuracy – When advice was labeled as AI-generated (vs. rad-generated), accuracy improved for both the IM/EM physicians and radiologists (+4.22% & +3.15%).
- Presumed AI Use Improves Expert Confidence – When advice was labeled as AI-generated (vs. rad-generated), radiologists were more confident in their diagnosis.
The Takeaway
This study provides solid evidence supporting the use of visual explanations, and bolsters the increasingly popular theory that AI can have the greatest impact on non-experts. It also revealed that physicians trust AI more than some might have expected, to the point where physicians who believed they were using AI made more accurate diagnoses than they would have if they were told the same advice came from a human expert.
However, more than anything else, this study seems to highlight the underappreciated impact of product design on AI’s clinical performance.
|




|
|
No Time for Downtime
HealthPartners understands “the domino effect of imaging,” so they worked with Merative to move to enterprise imaging that’s specifically built for high availability. See how the major Minnesota-based health care system decided to make this change, the steps they took to make sure they implemented it the right way, and the impact this transition had on their imaging operations.
|
|
Automating What Radiologists Can’t Stand
Ready to reduce your tedious, time‑consuming, repetitive tasks? Join Nuance on Wednesday, February 8 (12:00 p.m. ET) to see how its next-generation platform streamlines reporting tasks and helps deliver more consistent, higher quality reports.
|
|
- Abbreviated HCC MRI Paradigm Shift: A new Radiology study supported dynamic abbreviated MRI’s potential to create a “paradigm shift” for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) detection, showing that the quick scanning method accurately detects early HCC cases. In a multi-center validation with 299 patients, abbreviated MRI detected early-stage HCC patients with high sensitivity and specificity (88% & 89%). However, it performed far worse among HCC patients with decompensated cirrhosis than those with compensated cirrhosis (sensitivity: 64% vs. 94%).
- Adaptix’s Digital Tomosynthesis FDA: Adaptix announced the FDA clearance of its DT Orthopedic imaging system, paving the way for the portable imaging company’s commercial launch. The compact digital tomosynthesis imaging system produces 3D scans of hands, elbows, and feet at the point-of-care, reportedly reducing costs and radiation exposure. Armed with over $15M in funding, Adaptix plans to expand its DT imaging technology into new healthcare areas, including more orthopedic applications, new chest scanners for ICU and ED environments, and even dentistry systems.
- TIW’s SCMR Takeaways: The Imaging Wire spent a day at SCMR 2023 last week, discovering that it’s a vibrant conference given its relatively niche cardiac MRI focus. SCMR 2023’s roughly 1,500 attendees had plenty of sessions to choose from (including some attended by a stray cat) and a full exhibit hall that served as a reminder of how many CMR post-processing solutions exist. However, SCMR 2023’s most notable takeaway was the consensus that insufficient reimbursements are holding back cardiac MRI utilization, awareness, and access.
- Healthcare AI’s Cost Impact: A McKinsey and Harvard University report suggests that wider adoption of AI could reduce US healthcare costs by between $200B and $360B per year (5% to 10% of US healthcare spending). These cost reduction estimates are based on AI applications that are achievable within the next five years, but only if several barriers are addressed (lack of trust among patients and doctors, heterogeneous data, misaligned incentives).
- Visage Adds UW & Samaritan: Visage Imaging continued its U.S. health system client expansion, announcing Visage 7 Enterprise Imaging contracts with the University of Washington’s UW Medicine (7yr / $17.5M) and Oregon-based Samaritan Health Services (8yr / $8.4M). Both UW Medicine and Samaritan will fully deploy Visage’s solutions in the cloud (Open Archive, Workflow, Viewer), and will replace legacy PACS across their networks, with initial go-lives targeted for the second half of 2023.
- Incidental CAC’s Short-Term Risks: A new study out of the UK showed that patients with incidentally-detected coronary artery calcifications in non-contrast chest CTs have significantly greater CVD risks. Analysis of 717 patients (325 w/ CAC, 0 w/ known CVD) found that CAC patients had 26 CVD events and five deaths over 3.5 years, while non-CAC patients had just one event. Patients with CAC scores above 100 also had far greater risks of CVD events and all-cause mortality (HR: 5.7 & 1.7).
- The VA’s AI Action: The Federal News Network highlighted the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs’ growing investments in imaging AI. The article largely focused on the VA’s upcoming AI Tech Sprint competition, which provides VA imaging data to industry, academic, and VA participants with the goal of evaluating lung cancer and heart disease AI tools. The VA also just completed a successful AI prioritization pilot that might lead to a full rollout, and is operating other AI pilots focused on mammography and lung cancer screening.
- Nanox FUD: The retail investment websites and discussion forums that made Nanox (aka Nano-X) medical imaging’s hottest stock in 2020/2021 seemed to turn against the aspiring “disruptor” in recent weeks. Commenters on trader forums are increasingly scrutinizing Nanox’s technology, business model, and potential legal/regulatory threats, while a new Seeking Alpha editorial argues that Nanox has “no value potential for retail investors” and attributes its early stock surge to IPO-ing during “the age of corporate disruptors popularized by meme marketers.”
- PHE Ending in May: Well… the day has finally come. The Biden administration announced plans to terminate the public health emergency this spring, ushering in a new chapter in the government’s pandemic response. The Kaiser Family Foundation put together a detailed look at the implications of the announcement, including hospital incentives for treating COVID patients, relaxed state licensure requirements, and cost sharing for at-home tests.
- The Virtual Radiology Reading Room: A new study out of Medstar Georgetown highlighted the positive impact of their custom Virtual Radiology Reading Room (VR3), a Microsoft Teams-based virtual radiologist consultation system designed to replace phone consults and allow location flexibility. Six months after implementation, a survey of 40 referring providers and 27 radiologists revealed high overall approval rates (4.7 & 4.1 out of 5), while 70% of both groups unsurprisingly preferred VR3 to phone calls (just 4.5% & 11% preferred the phone).
- NTT DATA & Rhino’s Federated Network: Rhino Health and NTT Data are partnering to build a federated data network intended to provide researchers and AI developers “with access to healthcare data at scale.” The collaboration will combine NTT DATA’s Advocate AI imaging services with Rhino’s technology and federated data network.
|
|
Canon’s AiCE Reconstruction Challenge
Despite what we’ve been taught, acquiring high SNR MRIs doesn’t always mean longer scan times. Take Canon’s AiCE Deep Learning Reconstruction challenge and see if you can tell which of these brain MRI studies were performed in less scan time with the help of AiCE DLR.
|
|
- Are you seeing the complete picture with your outdated cardiac PET imaging? Check out this Siemens Healthineers patient story, showing how cardiac PET/CT revealed microvascular diseases in a patient who had normal uptake on his PET exam.
- When the VA adopts your technology nationwide, you know you’ve been making an impact. That’s exactly what’s happening with Riverain Technologies’ ClearRead CT, which will be implemented across the VA Lung Precision Oncology Program (22 hub and 87 spoke locations).
- The Hyperfine Swoop Portable MRI has been used to care for children with hydrocephalus at Uganda’s Cure Hospital since 2021, improving imaging access without exposing patients to ionizing radiation. Learn more about the Swoop’s hydrocephalus impact here.
- Faced with rising scan volumes and many elderly patients, Lake Medical Imaging implemented Subtle Medical’s Subtle MR efficiency solution across its eight MR scanners, allowing it to scan 40 additional patients per day while maintaining quality of care.
- United Imaging’s service organization is called Customer Success for a reason. Their mission is to think ahead, understand their customers’ goals and proactively help customers achieve them. They also store critical service parts in the U.S. and back up their promises with the United Performance Guarantee.
- Trying to figure out how your IT resources can handle increased AI adoption? This Blackford paper details how the cloud is helping radiology organizations scale their computing resources to support multiple AI applications or algorithms.
- After years of expansion, Montreal’s Imagix Radiology moved to Intelerad, allowing it to unify and modernize its radiology IT infrastructure, while improving its efficiency and data exchange capabilities. See what Imagix had to say about making the move to Intelerad here.
- Proper patient data anonymization and deidentification is a must, but it can be challenging to do while still retaining clinical relevance. See why Enlitic proposes an AI-based approach to deidentify and anonymize healthcare data (both pixel data and metadata), and how it would be valuable to your organization.
- Hybrid PET/CT imaging and deep learning have been home to significant technological progress in recent years, and GE HealthCare’s latest PET/CT platform brings these trends together by leveraging deep-learning image processing to achieve the highest PET sensitivity levels and TOF image quality.
- We may be entering a third wave of imaging AI’s rapid evolution, that brings a shift from narrow point solutions to comprehensive multi-finding AI systems. Join this discussion with annalise.ai Chief Medical Officer, Rick Abramson, MD, exploring how this transition could take place, how radiologist and VC perspectives on AI are changing, and how AI might continue to evolve in the future.
- Imaging’s cloud evolution didn’t happen all at once. This Change Healthcare animation details the history of digital imaging architectures, and how cloud-native imaging improves stability and scalability, ease of management, patient data security, and operating costs.
- Radiology is leading healthcare’s AI revolution, and yet many people in radiology are just starting to build their understanding of AI. That’s why Bayer published its truly Complete Guide to Artificial Intelligence in Radiology, detailing how AI can address radiology’s challenges, AI’s core use cases, and AI’s path towards adoption.
|
|
|
Share The Imaging Wire
|
|
Spread the news & help us grow ⚡
|
|
Refer colleagues with your unique link and earn rewards.
|

|
|
|
|
Or copy and share your custom referral link: *|SHAREURL|*
|
|
You currently have *|REFERRALS|* referrals.
|
|
|
|
|