|
Low Value Incidentals | Wearable Echo
January 26, 2023
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“Rather than a benefit of imaging, they are usually a harm.”
|
|
Matthew Davenport, MD, on the unintended consequences of incidental findings management.
|
|
|
|
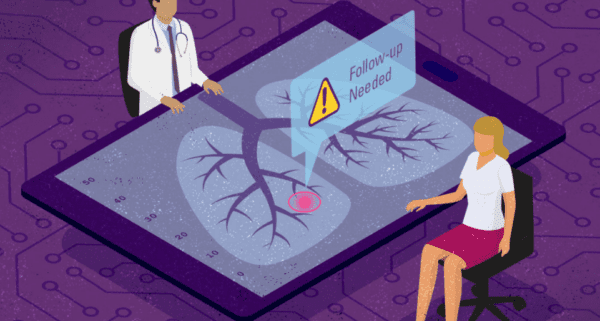
A whopping 15% to 30% of diagnostic imaging exams reveal at least one incidental finding. Each of those findings might seem like blessings to radiology outsiders, but a popular new AJR editorial argues that imaging incidentals are far more likely to drive low-value care.
Michigan Medicine’s Matthew Davenport, MD led-off his editorial by suggesting that early cancer detection “is not always an ideal outcome,” because most of those cancers won’t affect patient health, while incidental follow-ups always require resources and often negatively impact patients (physically, financially, and emotionally).
He identified numerous reasons for radiology’s incidental overdiagnosis challenges…
- Screening low-risk patients inherently uncovers low-risk incidentals
- There’s a lack of understanding of incidental risks (clinically and downstream)
- Many early cancers don’t or shouldn’t require treatment
- Radiologists face significant pressure to recommend follow-ups
Although many incidental findings significantly improve patient outcomes, and those positive examples have established incidentals as a “secondary benefit of imaging,” the editorial suggests that incidentals will have a negative overall impact on radiology’s value until current practices change.
So, what should we do? Dr. Davenport encourages radiologists to…
- Become more aware of the harms of incidental management
- Advocate for guidelines that emphasize high-value care
- Support research on incidental management practices
- “Avoid being alarmist” about incidentals in radiology reporting
- Adopt solutions to help rads assess incidental patients’ risk factors
- Balance diagnostic sensitivity with minimizing follow-up risks
The Takeaway
If you scroll through the Imaging Wire archives, you’ll find plenty of stories that depict incidentals as a net positive for patient care. In fact, most suggest that radiology’s research and business leaders are actively trying to find ways to detect more incidentals. However, efforts to better understand or to reduce incidentals’ negative impacts are far less common.
That divide is pretty notable given how many radiologists agree with Dr. Davenport, and it suggests that the barriers to solving incidental findings’ value problems are quite high.
|




|
|
Change Healthcare’s Secure Cloud
Did you know one quarter of healthcare organizations have experienced a cyber-attack in the last year? This Change Healthcare animation explains how 3rd-party certified cloud-native enterprise imaging can help secure IT infrastructure that might be exposed with re-platformed imaging systems.
|
|
- Wearable Cardiac Ultrasound: UCSD researchers developed a wearable cardiac ultrasound device that obtains continuous and real-time cardiac function data. The researchers designed the wearable ultrasound to enhance coupling with patients’ skin, allowing the left ventricle to be examined from different views while the patient is moving. They also developed a deep learning model that extracts LV volume from ultrasound recordings, producing waveforms of key cardiac performance indices such as stroke volume, cardiac output, and ejection fraction.
- 3D Cameras’ Positioning Advantage: A new Investigative Radiology study found that 3D patient positioning cameras do indeed improve CT patient positioning and reduce radiation exposure. The study of 3.1k chest and/or abdomen CTs revealed that 3D cameras significantly improved patients’ isocenter positioning compared to using visual laser-guided positioning techniques. 3D camera positioning also achieved higher absolute table height (165.6 vs. 170.0 mm), and reduced radiation dose length product (321.1 vs. 342 mGy), effective dose (3.3 vs. 3.5 mGy), and CT dose index (6.4 vs. 6.8 mGy).
- Explaining Contrast Vendors’ AI Surge: This week brought new insights into Bayer and Guerbet’s AI acquisitions, with editorials from Asher Orion Group’s John Kalafut PhD and Casey Insight’s Brian Casey. They explained that contrast vendors have been developing their AI strategies for a while (GE and Bracco too), and they are well positioned to target AI given their many imaging touch points, experience with complex hardware and software, strong financials, and imaging tech neutrality.
- PSMA PET/CT HCC Surveillance: A new study in Tomography added more evidence of PSMA PET/CT’s value monitoring hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which expresses PSMA. Among 19 patients with known or suspected HCC, PSMA PET/CT performed similarly to MRI and outperformed CT over a 12-month surveillance period, achieving 91% sensitivity (vs. 87% & 32%) and 70% specificity (vs. 73% & 100%). PSMA PET/CT’s 90% negative predictive value also surpassed MRI and CT (vs. 86% & 64%).
- The EU’s Cancer Imaging Initiative: The European Union launched its ambitious new European Cancer Imaging Initiative, which aims to facilitate the sharing of anonymized cancer imaging data, and support the development of digital technologies that improve cancer diagnostics and treatments (specifically AI and high-performance computing). The European Cancer Imaging Initiative will utilize a federated approach to link researchers and clinical sites, starting with 21 sites in 12 countries and later expanding to 30 data providers across 15 countries.
- Siemens and ASG’s UHF MRI Alliance: Siemens Healthineers and ASG Superconductors announced a partnership to co-develop ultra-high field MRI systems (>7T), with a goal to make ordering and installing UHF MRIs far more turnkey than what’s typically seen. The collaboration’s first project will be a 10.5T MRI system, which will be tested in ASG’s site in Italy, before being integrated and installed at a Chinese university by Siemens.
- ChatGPT Authoring Research: It didn’t take long for the AI world’s latest poster child, ChatGPT, to make its formal debut in scientific literature, and it’s already notched at least four authorship credits on published papers and preprints. As you might imagine, many scientists disapprove of the chatbot’s growing role as a research co-author, and publishers are now scrambling to regulate its use.
- CMRI AI’s PTT Potential: A new European Heart Journal study demonstrated that pulmonary transit time (PTT) – the time blood takes to pass from the right ventricle to the left ventricle – can be “easily, even automatically” obtained from stress perfusion cardiac MRIs using artificial intelligence. The team applied a PTT AI model to 353 patients’ routine stress perfusion CMRIs, automatically/accurately obtaining 266 patients’ PTTs, and showing that AI-based hemodynamic quantification might support future dyspnea and heart failure evaluations.
- Keya’s FFR-CT Clearance: Chinese imaging AI company Keya Medical announced the FDA clearance of its DeepVessel FFR solution, marking a rare addition to the U.S. FFR-CT segment. DeepVessel FFR analyzes CCTA exams to non-invasively assess coronary artery physiological function, and then generates a 3D model of the coronary artery tree and FFR-CT value estimates. Keya Medical might not be well known in the U.S., but it’s generated at least $110M in funding and is already approved for use in the EU and China.
- FDA Removes Shielding Recommendation: As radiology steadily moves away from gonadal shielding, the FDA officially removed its recommendation for the decades-old radiation protection practice. To support the change, the NCRP issued this pamphlet detailing the reasons for this change and how to explain it to patients.
- Hospital Outlook “Deteriorating”: Fitch Ratings maintained its “deteriorating” outlook for the not-for-profit hospital sector due to its diminishing financial reserves and business risks. The sector was originally downgraded from “neutral” last August as inflationary pressures compounded climbing labor and supply costs. While Fitch warned that these factors are raising questions about the liquidity of many health systems, there are also signs that “we are beginning to come out of the worst of it.”
|
|
Three Trends Driving In-Office MRI
Is your in-office MRI service prepared for the future? See how three macro trends will impact your in-office orthopedic MRI service, and the MRI capabilities you’ll need in the future in this Siemens Healthineers report.
|
|
How Aster DM Healthcare Leveraged CARPL
See how Dubai-based healthcare leader Aster DM Healthcare leveraged the CARPL platform to connect its doctors, data scientists, and imaging workflows, and support its AI projects and development infrastructure.
|
|
- AI delivers value to a wide range of healthcare stakeholders, but its primary value to health systems originate from its ability to automate tasks, democratize care, and deliver hard and soft ROI. See how these factors impact health systems’ bottom line in this Arterys report.
- Did you know that portable chest X-ray exams are responsible for 69% of patient misidentification errors in radiology? That’s why GE Healthcare’s AMX Navigate portable X-ray system features a handheld barcode reader, allowing technologists to scan a patient’s wristband and automatically match the patient to the worklist.
- Enterprise imaging is mainly adopted in the largest hospitals, but that doesn’t have to be the case. Check out this Imaging Wire Show featuring Novarad product leader Dave GrandPre, where we discuss what’s caused this divide and why smaller hospitals should adopt enterprise imaging.
- Proper patient data anonymization and deidentification is a must, but it can be challenging to do while still retaining clinical relevance. Join Enlitic and a panel of data anonymization experts on Tuesday, January 31 for an interactive discussion about how to do anonymization and deidentification the right way, plus a sneak peek into Enlitic’s upcoming anonymization product, Curie|ENCOG.
- Check out our interview with United Imaging CEO, Jeffrey Bundy, who explores company culture’s central role in medical imaging and how to build, improve, and maintain culture. If you’re ready to improve your organization’s culture, this interview is a great way to start.
- With radiation dose management now largely considered best practice, this Bayer white paper details the top five benefits of adopting contrast dose management.
- Can you tell which of these images are from a 3T MRI and which are from a 1.5T scanner and enhanced with Canon’s AiCE Deep Learning Reconstruction? Take the AiCE Challenge to find out.
- Curious how certain your AI is about its own finding? annalise.ai’s confidence bar displays the likelihood of each finding and the AI model’s level of certainty, helping clinicians perform their interpretations with greater confidence.
- With rising patient acuity rates creating “unsustainable financial challenges,” health systems are looking for innovative ways to increase critical care throughput. A growing number of health systems are achieving this goal with the Hyperfine Swoop point-of-care MRI, which can eliminate risks associated with intrahospital transport and keeps more critical care team members in the ICU.
- When Middlesex Health set out to adopt imaging AI, the Connecticut-based community hospital made the unique decision to start with non-interpretive AI solutions. See how that decision led them to Subtle Medical, and the impact it had with all of the hospital’s imaging stakeholders.
- Intelerad just launched its Intelerad Cloud suite of imaging solutions, marking the culmination of over four years of cloud investments and acquisitions. The new Intelerad Cloud allows imaging organizations to adopt a variety of hybrid, public, or private cloud solutions based on their specific needs (including: PACS, VNA, image exchange storage, long-term archiving, disaster recovery, patient portal).
|
|
|
Share The Imaging Wire
|
|
Spread the news & help us grow ⚡
|
|
Refer colleagues with your unique link and earn rewards.
|

|
|
|
|
Or copy and share your custom referral link: *|SHAREURL|*
|
|
You currently have *|REFERRALS|* referrals.
|
|
|
|
|