|
Multimodal Virtual Breast Biopsies| In-Home Ultrasound
November 3, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“Truth be told, AI isn’t intelligent. But will do the trick.”
|
|
A tweet by Amine Korchi MD.
|
|
|
Healthcare providers continue to demand solutions that make them more efficient, and that’s exactly what we discuss in the latest Imaging Wire show with Subtle Medical’s Ajit Shankaranarayanan. If you’re responsible for your organization’s imaging efficiency or think your team might benefit from faster scans, you should watch this video.
|
|
|
|
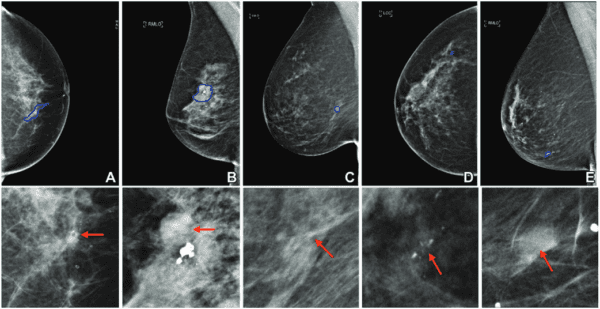
Radiology Journal detailed a multimodal AI solution that can classify breast lesion subtypes using mammograms, potentially reducing unnecessary biopsies and improving biopsy interpretations.
Researchers from Israel and IBM/Merative first pretrained a deep learning model with 26k digital mammograms to classify images (malignant, benign, or normal), and used these pretraining weights to develop a lesion subtype classification model trained with mammograms and clinical data. Finally, they trained a pair of lesion classification models using digital mammograms linked to biopsy results from 2,120 women in Israel and 1,642 women in the US.
When the Israel AI model was tested against mammograms from 441 Israeli women it…
- Predicted malignancy with an 0.88 AUC
- Classified ductal carcinoma in situ, invasive carcinomas, or benign lesions with 0.76, 0.85, and 0.82 AUCs
- Correctly interpreted 98.7% of malignant mammographic examinations and 74.6% of invasive carcinomas (matching three radiologists)
- Would have prevented 13% of unnecessary biopsies and missed 1.3% of malignancies (at 99% sensitivity)
When the US AI model was tested against mammograms from 344 US women it…
- Predicted malignancy with a lower 0.80 AUC
- Classified ductal carcinoma in situ, invasive carcinomas, or benign lesions with lower 0.74, 0.83, and 0.72 AUCs
- Correctly interpreted 96.8% of malignant mammographic examinations and 63% of invasive carcinomas (matching three radiologists)
The authors attributed the US model’s lower accuracy to its smaller training dataset, and noted that the two models’ also had worse performance when tested against data from the other country (US model w/Israel data, Israel model w/ US data) or when classifying rare lesion types.
However, they were still bullish about this approach with enough training data, and noted the future potential to add other imaging modalities and genetic information to further enhance multimodal breast cancer assessments.
The Takeaway
We’ve historically relied on biopsy results to classify breast lesion subtypes, and that will remain true for quite a while. However, this study shows that multimodal-trained AI can extract far more information from mammograms, while potentially reducing unnecessary biopsies and improving the accuracy of the biopsies that are performed.
|




|
|
Geisinger Health & Siemens Healthineers Expand MRI Access
When Geisinger Health set a goal to improve access to care, it leveraged Siemens Healthineers’ syngo Virtual Cockpit to ensure that its expert radiologic technologists were accessible to all 11 of its radiology facilities. Hear what Geisinger’s technologists and administrators had to say about how the remote scanning solution allowed them to extend hours and improve patient throughput.
|
|
Making AI Evaluations More Effective
If you’re in the business of using or providing AI, there’s a good chance you spend a lot of time managing AI evaluations. But are your evaluations as efficient or effective as they could be? Check out this Imaging Wire Show with Riverain Technologies CEO, Steve Worrell, detailing the best practices for mitigating AI adoption risks, today and into the future.
|
|
- The Future of In-Home Ultrasound: Signify Research forecasted that ultrasound will continue to expand into patient homes, although the timing and path of this expansion is still unclear. The firm highlighted growing investments from home ultrasound vendors, but noted the still unanswered questions about who will perform these exams (patients or professionals), who will pay for these devices and services, and how regulators will view this expansion. They also noted that it might depend on the application, as patients could handle obstetrics ultrasound but echo ultrasound is more appropriate for clinicians.
- Low COVID CXR Agreement: A study in European Radiology detailed COVID CXR assessments’ high variability, suggesting that CXRs alone might be ineffective for COVID triage – especially for indeterminate cases. Twenty readers of varying experience categorized 305 COVID CXRs, achieving low agreement with indeterminate categorizations (28%-37%), moderate agreement with classic/probable categorizations (49%-76%), and higher agreement with severe categorizations (65%-95%).
- VIDA & RAYUS Clinical Trials Alliance: Respiratory imaging AI clinical trials company VIDA Diagnostics and imaging center giant RAYUS Radiology announced a partnership that allows RAYUS’ +150 locations to serve as VIDA clinical trial imaging sites. RAYUS imaging centers will be connected to the VIDA Intelligence portal, helping imaging staff follow trial protocols. Although VIDA was originally a diagnostic AI company, it appears to have pivoted to a clinical trials AI strategy.
- Quibim’s QP-Prostate European Approvals: Quibim announced the CE Mark and UKCA approvals of its QP-Prostate solution for prostate cancer detection and diagnosis (already FDA cleared), allowing for its commercialization in the European and UK markets. QP-Prostate uses AI to support prostate MRI visualization and quantification, targeting improvements to MRI reporting efficiency, accuracy, and early detection.
- Edcetera Acquires Pulse Radiology: Online education company Edcetera acquired Pulse Radiology, expanding its healthcare offerings to radiologic technologist training. As part of Edcetera, Pulse Radiology will provide self-paced online courses for all ARRT certifications, continuing education, and post-certification development, while pairing RTs with its 1,100 affiliated imaging centers and hospitals for on-site training.
- Aidoc & Temple Health’s AI Alliance: Aidoc announced a new AI partnership with Philadelphia’s Temple Health system, which will integrate the Aidoc AI Care Platform across the system’s cardiovascular, neurosciences, and radiology service lines. The new Temple Health alliance continues Aidoc’s US health system expansion, following similar announcements with UofL Health, Wellspan Health, Atlantic Health, and Novant Health earlier this year.
- CCTA Heart Attack Differentiation: New research in Radiology revealed that CCTA-based quantitative plaque analysis could help clinicians differentiate between patients with type 1 and type 2 myocardial infarction. Among 327 patients with type 1 MI, type 2 MI, and chest pain but no MI (n= 155, 36, 136), the presence of low-attenuation coronary plaque was an independent predictor of type 1 MI (OR: 3.44). Patients with type 1 MI had higher total (44% vs. 35%), noncalcified (39% vs. 34%), and low-attenuation (4.15% vs. 1.64%) plaque burdens than patients with type 2 MI.
- Viz.ai & Us2.ai’s Echo Coordination: Viz.ai announced a partnership with Us2.ai that will combine Viz’s intelligent care coordination platform and image viewer with Us2.ai’s AI-driven echocardiography reporting solution, improving the speed and the coordination of care for patients with suspected heart disease. The alliance continues Viz.ai’s expansion into cardiovascular care and beyond its neuro origins (joining solutions for cryptogenic stroke, aortic disease, and pulmonary embolism), while adding to Us2.ai’s growing list of platform partners (joining Aidoc and Blackford).
- Singular’s 3Dicom MD Clearance: Singular Health Group announced the FDA clearance of its 3Dicom MD collaborative diagnostic viewer, setting the stage for its 2023 US launch. 3Dicom MD allows physicians across specialties to collaborate on advanced imaging exams (CT, MR, PET), leveraging its in-built remote control, VoIP calling, and text chat features.
- FDA AI’s Lacking Validation: A new Clinical Radiology study revealed that of the 151 imaging AI products cleared by the FDA in November 2021, just 64% used clinical data for their validations, and even fewer specified study patient demographics (4%), reported machine specs (5%), revealed if the study was multicenter (34%), or identified ground truth (51%). Although these stats might not surprise AI insiders, they also underscore the need to validate all FDA-cleared AI solutions.
- AI Metrics Adds $1.26M: Oncology imaging AI startup AI Metrics secured $1.26M in bridge financing – led by several radiologists – that it plans to use to support its R&D efforts. AI Metrics supports radiologists’ CT and MRI interpretations, improving the accuracy and efficiency of cancer treatment guidance exams.
|
|
How Thomas Jefferson Leveraged CARPL.ai
See how Thomas Jefferson University relied on CARPL.ai to accelerate its AI validation and clinical adoption in this presentation by informatics and AI leader, Dr. Paras Lakhani.
|
|
- annalise.ai’s Annalise CXR solution detects up to 124 findings in a single chest X-ray. See how it detects such a wide range of abnormalities using these demo studies… or upload your own CXR images.
- Ready to overcome the worklist paradox of choice? See how GE Healthcare’s Intelligent Workload Manager eliminates case selection decision-making burdens and helps reduce radiologist stress.
- We hear a lot about AI being the next big thing or being immature and overhyped. This set of Blackford Analysis editorials reviews the challenges that are still holding back imaging AI, and the areas that AI is delivering genuine clinical benefits.
- Contrary to popular belief, imaging’s interoperability problem might actually be a data governance problem. The good news is, Enlitic’s Curie|ENDEX helps solve this problem, allowing you to get the most out of our modalities, PACS, and AI without needing your other vendors to intervene.
- Raising awareness about breast cancer is an important mission, but this Intelerad editorial highlights the need to match awareness with action, helped by technology to improve screening workflows.
- “This clinical experience, in a real critical time, proved that this ultra-low-field strength MRI, portable and self-shielding, could image patients in the most difficult circumstances.” That’s one of the clinical perspectives shared by Hyperfine Swoop users in this ASNR 2022 panel.
- Ready to improve your mammography workflows? Arterys is the first and only cloud-native Breast AI provider, and its solution dramatically reduces 3D Mammography reading times, while supporting breast cancer detection, density measurements, and personalized risk assessments.
- Enterprise imaging is mainly adopted in the largest hospitals, but that doesn’t have to be the case. Check out this Imaging Wire Show featuring Novarad product leader Dave GrandPre, where we discuss what’s caused this divide and why smaller hospitals should adopt enterprise imaging.
- Check out our interview with United Imaging CEO, Jeffrey Bundy, who explores company culture’s central role in medical imaging and how to build, improve, and maintain culture. If you’re ready to improve your organization’s culture, this interview is a great way to start.
|
|
|
Share The Imaging Wire
|
|
Spread the news & help us grow ⚡
|
|
Refer colleagues with your unique link and earn rewards.
|

|
|
|
|
Or copy and share your custom referral link: *|SHAREURL|*
|
|
You currently have *|REFERRALS|* referrals.
|
|
|
|
|