|
RTs in the Spotlight | AI Data Harvesting
September 21, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“Radiology is like lion-tracking with less danger and more carpal tunnel.”
|
|
A tweet from Ben White, MD on how radiologists must train themselves to see what they are looking for.
|
|
|
|
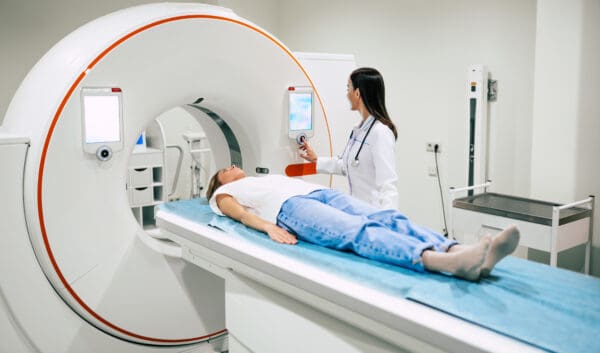
Radiographers and technologists were at the center of this week’s radiology news cycle, as three unrelated pieces highlighted the crucial role radtechs play, the significant challenges they face, and the actions required to help them succeed.
CXR Call to Action – After finding that nearly half of their portable chest X-ray images were “problematic,” a team of Stony Brook physicians issued a “call to action” to better support radiology technologists. Analysis of 500 portable CXRs found 231 problematic exams (46.2%), which most commonly occurred during overnight shifts (48%), and often stemmed from patient positioning issues.
- A focus group featuring six technologist department managers led the authors to propose three additional RT resources: (1) creating ongoing training programs focused on patient positioning, (2) assigning nurses to assist technologists during exams, 3) tasking internal medicine residents with reviewing CXRs before they’re sent to radiologists.
Big Teams, Little Training – The UK’s Society of Radiographers highlighted radiography managers’ struggles with high workloads and insufficient training (n = 200), finding that many of these leaders directly manage over 20 or 30 employees (52% & 40%… yikes) and never received manager training from their hospital (45%).
- The authors called these huge team sizes and lack of training a “gross miscalculation,” warning that it will cause managers to “undoubtedly fail in their duty of care to their staff,” especially considering that managers are often pulled into clinical duties due to understaffing.
Patient Safety’s Last Step – The WHO partnered with the ISRRT and ISR to emphasize radiographers and radtechs’ role as “the last step” in patient safety and medicine delivery, filling in gaps missed by radiation and magnetic safety experts. The collaborative webinar addressed radiographers/technologists’ responsibilities for ensuring safe contrast and radiopharmaceutical use, maintaining pediatric imaging best practices, and ensuring that pre-administration processes are complete before medication delivery.
The Takeaway
We talk a lot about modality-based approaches to improve radtech efficiency and reduce team burnout, and those are surely needed. However, this week’s news cycle was a solid reminder of HR’s role in technologist performance and what’s at stake if techs aren’t properly supported, trained, and staffed.
|




|
|
Unleash the Power of the Cloud
Change Healthcare’s cloud-native, zero-footprint Stratus Imaging PACS is live in clinical use. See how Stratus Imaging PACS is helping radiology practices improve productivity and patient care, while eliminating the cost and resource constraints of on-premise systems.
|
|
- Multi-Institutional Data Harvesting: Nature detailed a multi-institutional data harvesting (MIDH) method that was able to analyze imaging utilization and reporting trends across multiple health systems. The researchers repurposed Aidoc’s PE AI and NLP solutions to identify and evaluate CTPA exams performed at 13 US intuitions before and during COVID’s 2020 peak. The analysis revealed COVID-driven declines in CTPA exams (9,806 vs. 12,106) and a significant increase in PE positivity rates (11.6% vs. 9.9%), while showing how AI-based MIDH could help improve our understanding of how imaging is changing.
- Change’s Stratus Launch: Change Healthcare officially launched its cloud-native and SaaS-based Stratus Imaging PACS to the radiology practice market. This a key milestone for the cloud-centric PACS vendor, coming roughly one year after launching to beta users and two years after acquiring Nucleus.io. It could also prove to be a key milestone for radiology practices’ cloud adoption, noting how well their needs align with the cloud value proposition (security, IT labor, cost structure, speed), and the expanding field of practice-targeted cloud solutions that are now becoming available to them.
- Cardiac Nuclear-CT Guidelines: The ASNC and three other major nuclear imaging and cardiac CT societies released a new set of guidelines for using hybrid nuclear-CT cardiac imaging. The 45-page guideline goes step-by-step on how to prepare a lab for cardiac SPECT/CT and PET/CT imaging, including new recommended training requirements, models for cross-specialty study interpretation, and suggested solutions for reimbursement challenges.
- Incepto Adds €27M: French AI platform company Incepto raised €27M (total funding now €32.6M) to fund its expansion across Europe, including the creation of four new subsidiaries in Germany, Spain, Italy, and Portugal. Incepto will also use the funds to support its three strategic objectives: (1) creating a robust panel of AI partner solutions, (2) collaborating with physicians to develop applications that support unmet needs (e.g. knee MRI diagnostic assistance), and (3) supporting imaging organizations’ AI transformations.
- Incepto’s Partner Expansion: Speaking of Incepto’s goal to expand its partner list, the European AI platform company announced the addition of five new AI partners (IB Lab, Milvue, PAIRE, SmartSoft, Thirona) that expand its portfolio into key clinical areas (emergency care, oncology, orthopedics, rheumatology, and pneumology). These partnerships nearly double Incepto’s current list of seven AI partners, which includes a number of leading AI players (e.g. Subtle, ScreenPoint, Qure.ai, Aidence, Gleamer).
- Predicting PTC Recurrence with ETE: New research out of China found that clinicians can predict tumor recurrence in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) based on the presence of extrathyroidal extension (ETE) in ultrasound exams. Among 863 patients with PTC (59 w/ recurrence), preoperative lateral cervical lymph node metastasis was found more often in patients with ETE and extensive ETE detected, while microscopic ETE did not predict recurrence.
- New York’s Unused X-Rays: The state of New York spent $250M on medical technology during the COVID pandemic, including $86.4M on 1,179 X-ray machines, and all of these devices have gone unused since they were purchased in March 2020. That’s from a Politico report, also revealing that the National Guard is managing New York’s medical technology stockpile in warehouses, and there are no current plans to distribute them or put them to immediate use.
- DBT-Guided Biopsy Advantages: Johns Hopkins researchers showed that DBT-guided biopsies of suspicious breast calcifications produce similar clinical results as digital mammography-guided biopsies, but reduce patient discomfort and radiation exposure. Analysis of 1,310 patients’ biopsies (1,006 w/ DBT; 348 w/ DM) found no significant difference in malignancy rates (22% vs. 23%), while the DBT-guided biopsy had much lower procedure times (14.9 vs. 24.7) and total exposures (4.1 vs. 9.1).
- CT Nomogram Lung Cancer Detection: A new AJR study detailed a nomogram combining clinical data and CT-based radiomics that was able to accurately differentiate pneumonia from pneumonia-type invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma (IMA; a lung cancer). Using data from 314 patients for training, validation, and external testing (208 w/ pneumonia; 106 w/ pneumonia-type IMA), the nomogram differentiated the pneumonia types more accurate than a clinical model and two cardiothoracic radiologists (AUCs: 0.85 vs. 0.71 & 0.70 & 0.67).
- Konica Minolta’s DDR CSA Clearance: Konica Minolta announced the FDA clearance of its Chiropractic Straight Arm System, featuring the company’s unique dynamic digital radiography (DDR) technology, which allows clinicians to view anatomical movement from rapidly-acquired X-ray images. This might be the first chiropractic product launch we’ve covered, but DDR’s ability to show how bone and tissue interact over time seems to make it a good fit for this space (and the clinical MSK space too).
- Kaiser Scores Beat BI-RADS: A new study in EJR highlighted how Kaiser Scores (KS) can help clinicians accurately distinguish between malignant and benign breast lesions on contrast-enhanced mammography, avoiding up to 47.9% of unnecessary biopsies. Among 359 patients with breast lesions (231 malignant and 144 benign), the study’s two readers distinguished lesions with higher AUCs using KS compared to BI-RADS (Reader 1: 0.915 vs. 0.821; Reader 2:0.876 vs. 0.842).
|
|
- Despite significant interest, there’s still confusion about the value of imaging AI. This Blackford Analysis white paper explores the key cost considerations and ROI factors that radiology groups can use to figure out how to make AI valuable for them.
- Take the AiCE challenge and see why half the radiologists in a recent study “had difficulty differentiating” images from Canon Medical Systems’ Vantage Orian 1.5T MR using its AiCE reconstruction technology compared to standard 3T MRI images.
- Us2.ai’s echocardiography analysis automation solution is being integrated into the EchoNous Kosmos ultrasound platform, creating the most powerful diagnostic “power tool” ever created for the hand-carried POCUS market.
|
|
|
|
|