|
VERDICT MRI Slashes Biopsies | A Truly Mobile Fluoro-CT
August 10, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“These results are a massive leap forward for an exciting new test that could spare thousands of men each year unnecessary anxiety and pain.”
|
|
Prostate Cancer UK’s Dr. Matthew Hobbs on the VERDICT MRI technique’s potential to slash unnecessary biopsies.
|
|
|
|
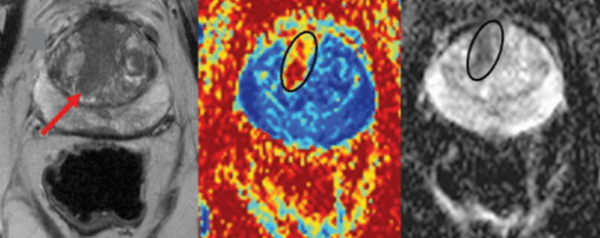
A new Radiology Journal study showed that VERDICT MRI-based analysis could significantly improve prostate cancer lesion characterization, and might solve PCa screening’s unnecessary biopsy problem.
Before we jump into the study… VERDICT MRI (Vascular, Extracellular, and Restricted Diffusion for Cytometry in Tumor) is a novel diffusion MRI modeling technique that estimates microstructural tissue properties, and has shown promise for cancer diagnosis and assessments. It can also be performed using standard 3T MRI exams.
The UK-based researchers had 165 men with suspected prostate cancer undergo mpMRI and VERDICT MRI (73 later confirmed w/ significant PCa). Over the 3.5yr study, they found that VERDICT MRI-based ‘lesion fractional intracellular’ volumes (FICs) have significant characterization advantages versus mpMRI-based apparent diffusion coefficient and PSA density measurements (ADC & PSAD):
- VERDICT MRI-based FICs classified clinically significant prostate cancer lesions far more accurately than ADC and PSAD (AUCs: 0.96 vs. 0.85 & 0.74).
- VERDICT-based FICs also clearly differentiated clinically insignificant and significant prostate cancer among the study’s Likert 3 lesions (median FICs: 0.53 & 0.18) and Likert 4 lesions (median FICs: 0.60 & 0.28), while ADC and PSAD measurements couldn’t be used to show which of these lesions would be cancerous.
The Takeaway
Noting that up to 50% of men with positive PI-RADS scores or >3 Likert scores end up with negative biopsy results, these findings suggest that VERDICT MRI could reduce unnecessary prostate biopsies by a whopping 90%.
That makes this study a “massive leap forward” for prostate cancer diagnostics, and provides enough evidence to make VERDICT MRI just one successful large multi-center trial away from clinical adoption.
|




|
|
Addressing the Unrealized Potential of Hanging Protocols
Wondering when someone will finally develop AI to address hanging protocol issues? The Enlitic Curie platform uses a standard imaging lexicon and a sophisticated algorithm to standardize DICOM metadata, making hanging protocols and automatic comparisons more consistent, and allowing radiologists to focus on image interpretation.
|
|
- Xoran’s Mobile Flouro-CT: Xoran Technologies announced the FDA clearance of its unique TRON mobile fluoroscopy-CT scanner. Xoran has big goals for the new “truly mobile” hybrid scanner, suggesting that TRON’s combination of modalities (full-body CT & fluoro) and its light/compact open-bore form factor, could better support some traditional healthcare settings (ORs, surgery centers, critical care units) while potentially democratizing imaging access globally.
- Bunker Shifts Make Shorter Lists: Radiology Associates of Northern Kentucky (RANK) detailed how adding “bunker shifts” reduced its worklists and minimized radiologist burnout. During these bunker shifts, a RANK radiologist clocks-in around 11am (usually weekdays) and works on complex cases without interruption (no calls, consultations, etc.) until they complete 40 wRVUs. Adopting bunker shifts significantly increased the percentage of days that RANK radiologists leave work on time (50% to 85%), while achieving a 100% employee approval rating and reducing overtime expenses.
- GE Brings Edison Accelerator to Canada: GE Healthcare expanded its Edison Accelerator program to Canada, teaming up with local digital health accelerator Nex Cube and six global imaging AI developers (16 Bit, Bot Image, CardioWise, contextflow, corelinesoft, Us2.ai) with the goals of supporting the AI startups’ integration into the Edison Platform and their path towards commercialization. This is GE’s fifth global Edison Accelerator (following US, EMEA, India, China), strengthening its AI portfolios and local startup relationships across these regions.
- CEUS-GB for FFL: We now have the strongest evidence yet that contrast-enhanced ultrasound-guided focal liver lesion biopsy is more accurate than ultrasound-guided biopsy (CEUS-GB & US-GB). A China-based randomized, controlled, multi-center study had 2,056 participants undergo either CEUS-GB or US-GB, finding that CEUS-GB had higher overall diagnostic accuracy (96% vs. 93%) and a significantly higher negative predictive value (74% vs. 57%). CEUS-GB’s accuracy advantage was even greater with smaller <2cm lesions (96% vs. 88%) and for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma in <2cm lesions (93% vs. 80%).
- Imaging’s Positive Q2: Most of the major OEMs’ healthcare/imaging divisions reported positive April-July performances. The period brought continued YoY revenue growth from Fujifilm’s medical systems business (+11.9% to $965M), GE Healthcare (+4% to $4.5B), and Siemens Healthineers’ imaging business (+2.5% to $2.68B), as well as rebounds from Konica Minolta’s healthcare division (+14% to $216M) and Canon Medical Systems (+5.8% to $893M). Meanwhile, Philips’ Diagnosis & Treatment division revenue fell for the second straight quarter (-4% to $2.2B) and Hologic’s breast imaging division declined significantly (-24.3% to $212.2M). More notably, division margins were solid for all vendors (6% to 18%) except Konica Minolta (0%).
- Stiff Heart Imaging Breakthrough: For the first time, clinicians can measure the efficacy of chemotherapy in patients with light-chain cardiac amyloidosis (stiff heart syndrome), thanks to the amyloid-measuring technique CMR Extracellular Volume Mapping (ECV). Researchers demonstrated that chemotherapy frequently reduced amyloid production, and CMR-derived measurements at six months independently predicted death (hazard ratio 3.82).
- Aquilion Serve’s Global Launch: Canon Medical announced the global launch of its new Aquilion Serve 80/160-slice CT scanner, leading with the 80cm-bore CT’s ease-of-operation, workflow efficiency, and image quality and consistency benefits. The Aquilion Serve inherits Canon’s prioritized AiCE AI-based image reconstruction technology, while also introducing the vendor’s new INSTINX workflow (reduces scan times & operator training) and the industry’s first 3D Landmark Scan (3D scan planning at dosage of 2D scanogram).
- Predicting Breast Cancer Chemo Response: A team of Spain-based researchers developed a series of machine learning models that used mpMRI-based imaging features and clinical variables to predict complete pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (pCR & NAC) among women with stage II-III breast cancer. When used with 58 women (12 w/ pCR), the combined model improved prediction accuracy compared to clinical or imaging-only models (91.5% accuracy, no false positives, 17% false negatives), suggesting that a technique like this could help avoid unnecessary treatment and surgery delays.
- The Inflation Reduction Act: What might end up being the biggest healthcare reform of the past decade recently passed the Senate with a 51-50 vote, sending the Inflation Reduction Act to the House for a final vote this Friday. The IRA would invest $64B to extend ACA subsidies through 2025, while also allowing Medicare to directly negotiate prices for the largest drugs (starting 2026) and placing a $2k cap on out-of-pocket drug costs for Part D beneficiaries (starting in 2025). Most healthcare groups welcomed the reform with favorable reactions, with the exception of Pharma, which called the plan a “tragic loss for patients.”
- Bot Image’s PCa FDA: AI startup Bot Image announced the FDA clearance of its ProstatID tool, which analyzes prostate MRIs to detect suspicious lesions, estimate cancer probability, and assign a PI-RADS score. Bot Image might not fit the profile of the next prostate cancer AI disruptor at first glance (based in Nebraska, 1 employee on LinkedIn, $1.4M in seed funding), although it’s actually a spinoff of established MRI coil developer ScanMed and included in the new GE Canada Edison Accelerator cohort covered above.
- Resident Physician Unions: Two JAMA editorials shed light on the rise of resident physician unions amid the increasing corporatization and consolidation of healthcare. The first editorial advised residents to consider the advantages of collective bargaining but warned that unions are “not a panacea,” while the second editorial emphasized how the culture of medicine perpetuates burnout and exacerbates the labor shortage.
|
|
- MR might be known for soft tissue imaging, but GE Healthcare’s oZTEo application is making one-stop soft tissue and bone imaging a reality. See how oZTEo works and how radiologists are approaching this new technology here.
- Ready to make MRI more accessible to your patients? See how Siemens Healthineers’ MAGNETOM Free.Max expands MR imaging to more patients, sites, and providers.
- Did you know one quarter of healthcare organizations have experienced a cyber-attack in the last year? This Change Healthcare animation explains how 3rd-party certified cloud-native enterprise imaging can help secure IT infrastructure that might be exposed with re-platformed imaging systems.
- Over 9 out of 10 people who should be screened for lung cancer aren’t, and nearly 50% of lung cancer cases are caught in the advanced stages. We know from prostate and breast cancer screening that clear guidelines and increased screening saves lives. But lung cancer screening has been challenging. Riverain strives to make everything about the lungs clearer, so they assembled this resource page for anyone interested in starting or improving their lung screening program.
- See how Novarad’s new VisAR augmented reality surgical navigation system enables physicians to find and reach their target destination more quickly – without the expense, footprint, and setup time of conventional navigation systems and robots.
- Despite significant interest, there’s still confusion about the value of imaging AI. This Blackford Analysis white paper explores the key cost considerations and ROI factors that radiology groups can use to figure out how to make AI valuable for them.
- After years of expansion, Montreal’s Imagix Radiology moved to Intelerad, allowing it to unify and modernize its radiology IT infrastructure, while improving its efficiency and data exchange capabilities. See what Imagix had to say about making the move to Intelerad here.
|
|
|
|
|