|
A Sweeping Ultrasound AI Acquisition | CT is Enough
July 27, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“It highlights the need for multiple pairs of eyes.”
|
|
Vanderbilt’s David Calkins, PhD on what a recent “normal blindness” study means for radiology.
|
|
|
|
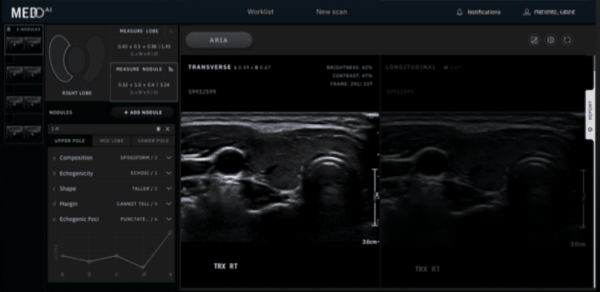
Exo took a big step towards making its handheld ultrasounds easier to use and adopt, acquiring AI startup Medo AI. Although unexpected, this is a logical and potentially significant acquisition that deserves a deeper look…
Exo plans to integrate Medo’s Sweep AI technology into its ultrasound platform, forecasting that this hardware-software combination will streamline Exo POCUS adoption among clinicians who lack ultrasound training/experience.
- Medo’s automated image acquisition and interpretation software has clearance for two exams (thyroid nodule assessments, developmental hip dysplasia screening), and it has more AI modules in development.
Exo didn’t disclose acquisition costs, but Medo AI is relatively modest in size (23 employees on LinkedIn, no public info on VC rounds) and it’s unclear if it had any other bidders.
- Either way, Exo can probably afford it following its $220M Series C in July 2021 (total funding now >$320m), especially considering that Medo’s use case directly supports Exo’s core strategy of expanding POCUS to more clinicians.
Some might point out how this acquisition continues 2022’s AI shakeup, which brought three other AI acquisitions (Aidence & Quantib by RadNet; Nines by Sirona) and at least two strategic pivots (MaxQ AI & Kheiron).
- That said, this is the first AI acquisition by a hardware vendor and it doesn’t represent the type of segment consolidation that everyone keeps forecasting.
Exo’s Medo acquisition does introduce a potential shift in the way handheld ultrasound vendors might approach expanding their AI software stack, after historically focusing on a mix of partnerships and in-house development.
The Takeaway
Handheld ultrasound is perhaps the only medical imaging product segment that includes an even mix of the industry’s largest OEMs and extremely well-funded startups, setting the stage for fierce competition.
That competition is even stronger when you consider that the handheld ultrasound segment’s primary market (point-of-care clinicians) is still early in its adoption curve, which places a big target on any products that could make handheld ultrasounds easier to use and adopt (like Medo AI).
|




|
|
Automating Echo AI
Check out this Imaging Wire Show featuring Us2.ai’s co-founders, James Hare and Carolyn Lam MBBS, PhD, detailing Us2.ai’s unique origins, impressive capabilities, and big goals to automate echocardiography reporting across the world.
|
|
An Image Sharing Starting Point
Imaging providers who want to finally #ditchthedisk can now start off with Novarad’s CryptoChart Lite solution, a no-cost version of CryptoChart built for providers transitioning to imaging sharing.
|
|
- CT is Enough for AIS: A JAMA-published study found CT scans might be sufficient for diagnosing patients with acute ischemic stroke, even though over 90% of these patients undergo both CT and MRI. Analysis of 246 AIS patients (50% CT, 50% CT+MRI) found that CT-only patients had lower incidence of death or dependence by the time of their discharge (42% vs. 48%) and a lower rate of stroke or death within the next year (12.5% vs. 19.5%).
- Point of Care Coordination: Viz.ai announced a partnership with Hyperfine that will combine Viz’s intelligent care coordination platform and image viewer with the Hyperfine Swoop Portable MR Imaging System. The combined solution would route bedside MRI exams to neuro care teams, with the goals of decreasing time to treatment and streamlining clinical workflows. Given Hyperfine’s ability to expand MRI to new areas of hospitals and Viz.ai’s ability to support imaging-based care coordination (no matter where scans are performed), this alliance makes a lot of sense.
- Mammography Screening’s Modest Overdiagnoses: A new study out of the UK suggests that mammography screening’s overdiagnosis rate might not be as high as some fear. Researchers analyzed data from 163k English women who participated in the NHS Breast Screening program (57K w/ breast cancer), finding that screening participants had a 9.5% overdiagnosis rate (3.7% when adjusted for self-selection), which the authors described as “at worst modest.”
- Cleerly’s $192M Funding Round: Coronary CTA AI startup Cleerly just closed a colossal $192M Series C round, quadrupling its Series B efforts and catapulting its total funding to $249.5M. Armed with the new investment, Cleerly plans to build out its team, expand the software’s commercial reach, and support over a dozen ongoing clinical trials. The massive VC backing is a testament to Cleerly’s potential to identify early-stage and asymptomatic heart disease.
- Improving Follow-up Adherence: A new JAMA study found that referring physicians don’t follow at least 12.5% of recommendations in radiology reports, while detailing what makes recommendations more (or less) likely to be acted upon. The review of 598 radiology reports, found that recommendations were more likely to be followed if they (1) don’t include any contingency language, (2) do specify shorter recommended follow-up times, and (3) show evidence of direct communication between the radiologist and referrer. They also recommended using structured reports with dedicated recommendation sections and a system to classify and track loop closures.
- MDD MRI Advantage: A new CARPL.ai-led study highlighted multidimensional diffusion MRI’s superior quantification and visualization of tissue microstructure, suggesting that MDD MRI could improve neurological disorder diagnoses. Analysis of nine existing MDD MRI studies revealed that the novel MRI technique’s microstructural tissue characterizations might be able to enhance clinicians’ ability to characterize a range of neurological indications (e.g. brain tumors, epilepsy, schizophrenia, MS, Parkinson’s, etc.).
- 3M’s Healthcare Spin Out: After months of rumors that 3M was exploring options to offload its healthcare business, the company officially announced that it will spin out the unit as a standalone entity by the end of 2023. The new entity will include 3M’s wound care, dental, health-IT, biopharma filtration products ($8.61B in combined revenue last year), with the new structure designed to “make both companies well positioned to pursue their respective priorities.”
- Mixed Self-Compression Results: A new study in European Radiology found that when women control their mammography compression (n=495; 245 w/ self-compression), they apply more force (114 vs. 102.5 daN) and achieve similar image quality compared to when technologists apply compression. However, women in the self-compression group didn’t achieve lower glandular dosage (1.90 vs. 1.93) and weren’t more likely to attend follow-up screening appointments, which have been seen as potential upsides of self-compression.
- Total-Body Theranostics: Michigan-based theranostics startup BAMF Health reached a key milestone this week, scanning its first nine men with prostate cancer using United Imaging’s uEXPLORER total-body PET and Telix’s new Illuccix PSMA-PET imaging agent. The exams are one part of BAMF Health’s theranostics launch, which will start with patients with prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors this summer, and expand to a wide range of personalized treatments in the future (e.g. Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, cardiac diseases, endometriosis, chronic pain).
- Radiologists Start High: A new AMN Healthcare report revealed that radiologists’ starting salary jumped by 13.5% in 2021/2022 to $455k, giving rads one of the top starting salaries after gastroenterologists, urologists, and orthopedic surgeons ($474k, $510k, $565k).
- Reconstructing Dynamic CTP: Deep learning image reconstruction may improve upon key challenges associated with dynamic CT perfusion. A team of Japan-based researchers applied DLR to 30 dynamic CTP scans and found that it reduced image noise by 20% (compared to iterative reconstruction) while still accurately capturing myocardial blood flow. That’s notable given that dynamic CTP is far superior to static CTP for measuring myocardial blood flow, but it also exposes patients to more radiation, forcing teams to rely on iterative reconstruction at the expense of image quality.
|
|
Becoming Imaging AI Adopters
We talk a lot about radiology practices’ AI adoption, but usually don’t have much evidence to back it up. That changes with this new Arterys report detailing how and why 30 US radiology groups became imaging AI adopters.
|
|
Taking Nuclear Medicine into the Future
We’re excited to share the latest Imaging Wire Show, featuring Siemens Healthineers’ Sebastian Ricci.
We explore how Siemens Healthineers is addressing molecular imaging’s biggest trends and challenges, the continued theranostics evolution, and much more. This is a must-watch episode if you’re in nuclear medicine, so check it out.
|
|
- See how GE Healthcare’s CT lineup is helping radiologists and technologists become more efficient through effortless workflow, new AI efficiencies, and a unique approach to scanner modularity.
- Pediatric patients can’t always accurately describe their orthopedic-related pain. Read how Lorenzo Biassnoi, MD, describes how SPECT/CT can help in this SPECT/CT and pediatric orthopedic surgery story.
- Hyperfine’s Swoop Portable MR Imaging System is redefining MR accessibility, but do you know how the Swoop is actually being used? Check out this case study detailing the clinical settings and patient scenarios that the Swoop is supporting today.
- Find out what built for the modern world means — and why it matters — in this Aunt Minnie profile on United Imaging’s more modern approach to vertical integration, leadership, and culture.
- Imaging’s cloud evolution didn’t happen all at once. This Change Healthcare animation details the history of digital imaging architectures, and how cloud-native imaging improves stability and scalability, ease of management, patient data security, and operating costs.
- See how Einstein Healthcare Network reduced its syringe expenses, enhanced its syringe loading, and improved its contrast documentation when it upgraded to Bayer Radiology’s MEDRAD Stellant FLEX CT Injection System.
- Over a three-year proof of concept study, UT Health San Antonio found that Enlitic’s Curie Standardize solution would reduce its average CT (head, chest, abdomen) study organization time from 25 to 9 seconds. That adds up when multiplied over 480k annual studies.
- Adopting a platform strategy can simplify the deployment and management of imaging applications and AI algorithms, but there’s a lot to consider. In this eBook, Blackford Analysis and its clients detail how AI platforms can benefit clinical and IT teams, and share guidelines to consider when selecting a platform.
|
|
|
|
|