|
Echo AI Variability | Demanding Image Access
July 24, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“I humbly submit a draft proposal for a new multimodality standardized radiology grading schema: Sigh-RADS.”
|
|
Ben White, MD proposing a new way to measure sigh-inducing imaging orders.
|
|
Taking Nuclear Medicine into the Future
We’re excited to share the latest Imaging Wire Show, featuring Siemens Healthineers’ Sebastian Ricci.
We explore how Siemens Healthineers is addressing molecular imaging’s biggest trends and challenges, the continued theranostics evolution, and much more. This is a must-watch episode if you’re in nuclear medicine, so check it out.
|
|
|
|
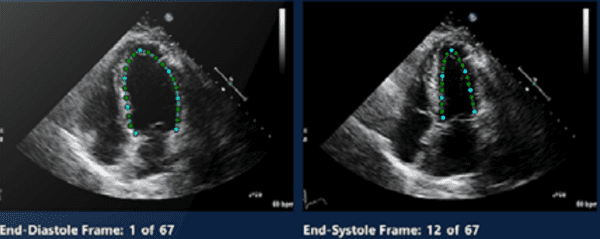
A new JASE study showed that AI-based echocardiography measurements can be used to predict COVID patient mortality, but manual measurements performed by echo experts can’t. This could be seen as yet another “AI beats humans” study (or yet another COVID AI study), but it also gives important evidence of AI’s potential to reduce echo measurement variability.
Starting with transthoracic echocardiograms from 870 hospitalized COVID patients (13 hospitals, 9 countries, 27.4% who later died), the researchers utilized Ultromics’ EchoGo Core AI solution and a team of expert readers to measure left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and LV longitudinal strain (LVLS). They then analyzed the measurements and applied them to mortality prediction models, finding that the AI-based measurements:
- Were “significant predictors” of patient mortality (LVEF: OR=0.974, p=0.003; LVLS: OR=1.060, p=0.004), while the manual measurements couldn’t be used to predict mortality
- Had significantly less variability than the experts’ manual measurements
- Were similarly “feasible” as manual measurements when applied to the various echo exams
- Showed stronger correlations with other COVID biomarkers (e.g. diastolic blood pressure)
- Combined with other biomarkers to produce even more accurate mortality predictions
The authors didn’t seem too surprised that AI measurements had less variability, or by their conclusion that reducing measurement variability “consequently increased the statistical power to predict mortality.”
They also found that sonographers’ original scanning inconsistency was responsible for nearly half of the experts’ measurement variability, suggesting that a combination of echo guidance AI software (e.g. Caption or UltraSight) with echo reporting AI tools (e.g. Us2.ai or Ultromics) could “further reduce variability.”
The Takeaway
Echo AI measurements aren’t about to become a go-to COVID mortality biomarker (clinical factors and comorbidities are much stronger predictors), but this study makes a strong case for echo AI’s measurement consistency advantage. It’s also a reminder that reducing variability improves overall accuracy, which would be valuable for sophisticated prediction models or everyday echocardiography operations.
|




|
|
Hyperfine Images Intelligently
Hyperfine’s Swoop Portable MR Imaging System might look like hardware, but its deep learning-based image reconstruction pipeline is what makes the MRI’s point-of-care performance possible. See how Hyperfine’s reconstruction technology improves image quality, while allowing advanced gridding and denoising.
|
|
Canon Across America
Canon Medical is making its way through the US on its 2022 Mobile Tour, bringing its products and solutions directly to hospitals and providers in 50 US cities. Tune in to see when Canon is coming to you and watch highlights from its tour stops along the way.
|
|
- Patients Want Access: A new PocketHealth report (n=242) revealed strong evidence that patients benefit from access to their healthcare information. Before the respondents had access to their medical records, only 27% were able to see their imaging, and among them 64% only received images via CDs and 52% had difficulty sharing images with their care teams. After these patients gained access to their medical records, 77% found it easier to access their imaging and 27% found it easier to share their imaging. Gaining access to imaging also made patients feel more informed, engaged, and have greater peace of mind (75%, 61%, >50%).
- RapidAI’s Hyperdensity FDA: RapidAI secured FDA clearance for its Rapid Hyperdensity AI tool, which allows physicians to use non-contrast CT scans to quickly assess the severity of acute neurological conditions such as traumatic brain injuries and intracranial hemorrhage. Rapid Hyperdensity helps hospitals and mobile stroke teams triage patients by providing additional contextual information, automatically detecting intracranial hyperdensities (>1ml), and allowing results to be viewed through their Rapid mobile app, PACS, or email.
- Micro-US + mpMRI: A new Radiology-published study suggests that micro-ultrasound might prove to be an “attractive addition” to multiparametric MRI for detecting clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa). Among 94 men with suspected prostate cancer, mpMRI and micro-US identified a similar number of men with csPCa (37 vs. 33), clinically insignificant prostate cancer (14 vs. 15), and cribriform / intraductal PCa (14 vs. 13). However, mpMRI avoided far more biopsies (32 vs. 9).
- GE Voluson Expert 22: GE Healthcare unveiled its Voluson Expert 22 ultra-premium women’s health ultrasound system, which launches with improvements to its image quality, operational efficiency, user interface, and user experience. GE specifically highlighted the image quality advantages of the Voluson Expert 22’s Lyric Architecture (higher-res, more detailed, deeper imaging), and the workflow efficiency of its embedded AI apps (reduces key workflows by 65% to 81%).
- Simplifying CXR Transfer Learning: Google Health unveiled its CXR Foundation transfer learning tool, intended to make it easier to train chest X-ray AI models. CXR Foundation uses advanced ML methods to generate pre-trained “CXR networks” that convert CXR images to “embeddings” (i.e. information-rich numerical vectors) that require less data and computational resources for model development. To prove it, Google Health used the tool to train CXR AI models to detect tuberculosis with only 45 CXR images and predict COVID-19 outcomes with just 528 images.
- AdvaHealth & Mach7’s Cloud Alliance: AdvaHealth Solutions and Mach7 Technologies announced a strategic partnership, combining AdvaHealth’s AdvaPACS cloud-native PACS with Mach7’s eUnity zero-footprint diagnostic viewer, creating an end-to-end cloud solution that will likely target AdvaHealth’s Asia Pacific market.
- Viz.ualizing the Contrast Shortage: Viz.ai made the iodinated contrast shortage feel a lot more tangible in a recent post, showing that hospitals that use GE contrast have reduced their overall CTA and CTP study volumes by ~20% and ~60%, respectively. If you’re wondering whether other contrast manufacturers have been able to fill in the GE supply gap, the report’s chart makes it very clear that they haven’t made much of an impact yet.
- CMRI’s Hypertension Biomarkers: A new study out of Singapore showed that cardiac MRI-detected myocardial fibrosis is associated with greater risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes among patients with hypertension. The researchers performed CMRIs on 786 patients with hypertension, finding that 45 (18%) had nonischemic late gadolinium enhancement (LGE). These nonischemic LGE patients had a higher risk of future adverse outcomes (acute coronary syndrome, heart failure hospitalization, strokes, and cardiovascular mortality) within a 39-month median follow-up period (hazard ratio: 6.69).
- Aidoc & UofL Health’s AI Alliance: Aidoc announced a new AI partnership with Kentucky’s UofL Health, revealing plans to integrate six AI modules (ICH, PE, incidental PE, c-spine fracture, rib fractures, intra-abdominal free gas) via the Aidoc AI Care Platform. UofL Health’s Aidoc partnership appears to be part of its increased commitment to imaging AI, coming a few months after the University of Louisville opened its Center for AI in Radiological Sciences (CAIRS).
- Radialis’ Organ-Targeted PET: Radialis announced the FDA clearance of its unique Radialis PET Imager, which images a range of specific organs and anatomy (breast cancer, lymph nodes, neuro, heart, etc.), and is highlighted by its high image quality, support for any PET radiotracer, and small footprint (6×2.5×4.5 ft). Radialis positions its new organ-targeted PET as a complement to traditional PET/CT systems within nuclear medicine fleets.
- Data Breaches Cool Off: Health data breaches have begun to pull back from the record levels set in 2021. Fortified Health Security counted 337 breaches that impacted more than 500 records through the first half of the year (down from 368 last year), but the percentage of incidents linked to malicious attacks climbed from 73% to 80%. Healthcare providers saw the largest share of breaches (72%), followed by business associates (16%), and health plans (12%). It appears that imaging center company, Shields, was responsible for H1’s largest health data breach (2M patients).
|
|
Addressing the Continuum of Care
See how Enlitic is improving the entire continuum of care by attacking the core issues of data standardization, accessibility, interoperability, and availability,
|
|
- See how Valley Radiology’s decision to make Intelerad IntelePACS its single reading environment helped the independent practice gain control of its growing volumes and rising case complexity, improve its efficiency and radiologist experience, and deliver better patient care.
- Us2.ai recently announced the global launch of its flagship echocardiography AI solution, leveraging a new $15M Series A round, and its unique abilities to completely automate echo reporting (complete editable/explainable reports in 2 minutes) and analyze every chamber of the heart (vs. just left ventricle with some vendors).
- Clinicians are using the NAEOTOM Alpha to overcome limitations previously thought unavoidable in CT, with ultra-high spatial resolution without dose penalty and detailed spectral imaging without compromises. Get the facts about the technology and the benefits of photon-counting CT.
- In this Novarad video, interventional oncologist Gary M. Onik, MD shares how Novarad’s AR surgical navigation system, OpenSight, helps his team accurately assess and treat tumors.
- Find out what built for the modern world means — and why it matters — in this Aunt Minnie profile on United Imaging’s more modern approach to vertical integration, leadership, and culture.
- When SyntheticMR validated its SyMRI MSK solution, they leveraged the CARPL platform to compare conventional knee and spine MRI image quality with SyntheticMR images. Check out their validation process and results here.
|
|
|
|
|