|
Content-Based AI Efficiency | Testing Incidental PE
July 13, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“Standardized reports do not, I repeat DO NOT, standardize radiologist’s competence.”
|
|
A tweet from Penn Medicine radiologist, and believer in the competence curve, Saurabh Jha, MD.
|
|
|
|
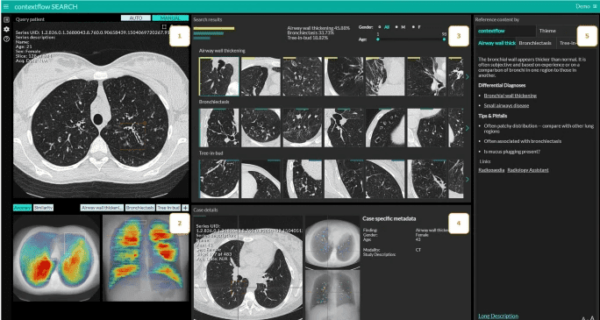
A new study out of Austria provided solid evidence that content-based image retrieval systems (CBIRS) enhance radiologists’ reading efficiency, while potentially improving their diagnostic accuracy.
Eight radiologists reviewed chest CTs from 108 patients with suspected diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), leveraging contextflow’s AI-based SEARCH Lung CT CBIRS with half of the exams.
Using the radiologists’ CT image regions of interest, the CBIRS would search a database of 6,542 chest CTs to identify similar scans, providing the rads with the three most likely disease patterns and supporting information (e.g. a list of potential differential diagnoses). The CBIRS’ added “context” had a notable impact on the radiologists:
- Reducing their average reading time by 31.3% (197 vs. 287 seconds)
- Reducing resident and attending radiologists’ reading time by 27% and 35%
- Improving overall diagnostic accuracy by over 7pts (42.2% vs. 34.7%; not statistically significant)
These reading time reductions came despite the fact that radiologists were more likely to search for additional information when using the CBIRS (72% vs. 43% of cases). That’s partially because CBIRS allowed greater speed improvements when radiologists searched for more information (110 seconds faster vs. without CBIRS) than when rads didn’t search for more info (39 seconds faster).
The Takeaway
This study presents a rare example of how imaging AI can significantly improve radiologists’ efficiency, while amplifying their current workflows and diagnostic decision-making processes. It’s also the second study in the last year suggesting that CBIRS might improve diagnostic accuracy, although the authors encourage more research into CBIRS’ accuracy impact to know for sure.
|




|
|
DRC Unifies with Intelerad
Faced with growing subspecialty volumes, Diversified Radiology of Colorado adopted Intelerad’s InteleOne XE enterprise workflow solution to ensure all appropriate cases are read by subspecialists, while reducing its average TAT to under 17 minutes.
|
|
- Philips’ MR SmartSpeed FDA: Philips announced the FDA clearance of its SmartSpeed MR image reconstruction software, which reconstructs full images from under-sampled MR data to significantly improve image resolution or scan speed times (+65% & +3x). The AI-based addition to Philips’ Compressed SENSE engine also boasts compatibility with 97% of clinical MR protocols.
- Multi-Modal COVID AI: A team of global researchers developed a chest X-ray and EHR-based ML model that accurately predicts COVID patients’ 30-day mortality risks. The EHR/CXR fusion model was trained using data from 2,547 patients at a Madrid hospital, and then tested against data from hospitals in South Korea and New Jersey (n = 336 & 242), achieving higher AUCs than EHR and CXR-only models (NJ: 0.76 vs. 0.74 & 0.72; S. Korea: 0.95 vs. 0.92 & 0.90). Noting COVID AI’s bad reputation, the authors did a great job detailing their training process.
- Canon Acquires NXC Imaging: Canon Medical Systems USA expanded its presence across the upper Midwest with its acquisition of Minnesota-based distributor, NXC Imaging. Canon and NXC Imaging were already very close, following 33 years of partnership that has become nearly exclusive (NXC also carried Ziehm C-arms). That said, the acquisition still improves Canon Medical’s direct presence in the region and supports its strategy to “continue building its substantial sales and service organization.”
- VSI Ultrasound’s Accessibility Advantage: A study published in the Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine found that the volume sweep imaging (VSI) ultrasound protocol might improve access to care by enabling inexperienced operators to provide diagnostic-quality images of palpable breast lesions. The study had medical students use VSI on 160 patients after less than two hours of training, producing video clips that allowed radiologists to diagnose breast lesions with 97% sensitivity and 100% specificity, corresponding to 97.6% agreement with standard of care.
- Aidoc & Isala’s AI Alliance: Aidoc announced a new partnership with Isala Hospital, one of the Netherlands’ largest non-academic medical facilities, revealing plans to integrate three AI triage and notification modules (ICH, PE, c-spine fracture). Isala highlighted Aidoc’s willingness to demonstrate performance and constantly improve its algorithms as one of its reasons for entering the partnership.
- Tumor Doubling Time: A Stanford study showed that tumor volume doubling time (TVDT), measured by comparing tumors in previous and current DBT mammograms, could be used to distinguish between benign and malignant tumors. The researchers analyzed DBTs from 28 patients with invasive ductal or lobular carcinoma and 40 patients with benign lesions, finding that TVDT was significantly shorter for malignant breast cancers (<1yr doubling time = 6.33 OR of invasive cancer). The authors conclude that TVDT assessments could help reduce unnecessary imaging and biopsies for lesions with longer doubling times.
- ImaCor & Clarius’ TEE Solution: Hemodynamic ultrasound startup ImaCor and handheld ultrasound company Clarius launched a partnership that will make ImaCor’s FDA-cleared transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) system available in a handheld format. Previously only available with cart-based ultrasounds, ImaCor’s Zura Handheld Hemodynamic Ultrasound and ClariTEE transesophageal echo probe now operate with the Clarius Ultrasound App, allowing handheld operation and mobile device viewing.
- QUSTom Initiative: European researchers launched a new R&D initiative called QUSTom (Quantitative Ultrasound Stochastic Tomography) that uses ultrasound and supercomputing to create an alternative to current imaging techniques such as mammograms for breast cancer detection. The project received €2.7M in funding from the European Innovation Council and researchers suggest that QUSTom will offer superior image quality and better monitoring of tumors, while eliminating radiation risks.
- Nuance’s AI Visualize Case Dismissed: A US District Judge dismissed AI Visualize’s patent infringement lawsuit against Nuance and Mach7, alleging that Mach7’s eUnity diagnostic viewer and Nuance’s PowerShare platform (which integrates with eUnity) infringed on AI Visualize’s patents related to “fast access to advanced visualization of medical scans using a dedicated web portal.” Nuance’s lawyers successfully argued that AI Visualize’s patents were based on an “abstract idea” that can’t be enforced under patent law.
- Testing Incidental PE AI: A new AJR study showed that AI tools could be used to catch more incidental pulmonary embolism (iPE) cases by screening chest CTs performed for other reasons (not using CTPAs). The researchers used Aidoc’s iPE detection tool to review 3,003 contrast-enhanced chest CTs from 2,555 patients, finding that it detected iPEs with lower specificity and PPV than the radiology reports (92.7% vs. 99.8%; 86.8% vs. 97.3%), but achieved statistically similar sensitivity and NPV (82.5% vs. 90.0%; 99.8% vs 99.9%). Out of 40 iPEs, Aidoc caught four that radiologists missed and seven were only detected by radiologists.
- Hospital Margins Update: Kauffman Hall’s latest National Hospital Flash Report shows that rising supply and labor costs contributed to the fifth consecutive month of negative hospital margins, which averaged -0.33% in May. Although gross operating revenues rose by 3% with a 4.8% month-over-month rise in patient days, the increase was not enough to offset the rising costs that are expected to keep margins below pre-pandemic levels for the rest of the year.
|
|
Solving AI’s Adoption Challenges
The flow of new AI applications makes it hard for radiology groups to determine which tools would help them and how IT teams can handle increased AI adoption. In this Blackford Analysis white paper, radiology and IT leaders from NYU and Canopy Partners share how a platform approach alongside a curated marketplace can help solve these challenges.
|
|
- Pediatric patients can’t always accurately describe their orthopedic-related pain. Read how Lorenzo Biassnoi, MD, describes how SPECT/CT can help in this SPECT/CT and pediatric orthopedic surgery story.
- See how 2-meter total body PET gives molecular imaging teams a diagnostic advantage compared to other “eyes to thighs” PET options in this editorial by United Imaging CEO Jeffrey M. Bundy.
- After setting ambitious regulatory and commercialization goals, Lunit leveraged CARPL.ai’s platform and operational guidance to complete the clinical trials needed for its INSIGHT CXR and MMG AI tools’ FDA clearances.
- Imaging AI deployments face a long list of challenges that often emerge before any value is delivered. This Enlitic post details the top 10 AI deployment challenges organizations must understand in order to make sure their own deployments are successful.
- Take the AiCE challenge and see why half the radiologists in a recent study “had difficulty differentiating” images from Canon Medical Systems’ Vantage Orian 1.5T MR using its AiCE reconstruction technology compared to standard 3T MRI images.
- Hyperfine’s Swoop Portable MR Imaging System is redefining MR accessibility, deploying MR-enabled decision-making across clinical settings within minutes. But do you know how the Swoop is actually being used? Check out this clinical case study detailing the settings and patient scenarios that the Swoop is supporting today.
|
|
|
|
|