|
AI Underwriting | No Doctor Required
July 10, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“Outlier detection in deep neural networks is, mostly, magic pudding thinking.”
|
|
Our favorite AI safety expert, Dr. Lauren Oakden-Rayner, on why autonomous AI might be wishful thinking.
|
|
Introducing Cardiac Wire
We’re thrilled to introduce our third newsletter, Cardiac Wire. Starting today we’ll be delivering the most important news in cardiology – curated and written with the typical “Wire” style.
The first edition hits inboxes in a few hours, so if you’re interested in cardiology and want an easier way to stay informed, subscribe to get Cardiac Wire here.
|
|
|
|
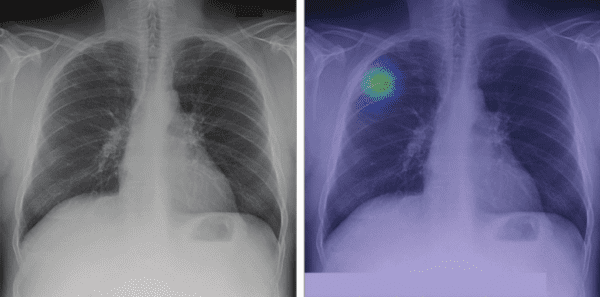
Cathay Life Insurance will use Lunit’s INSIGHT CXR AI solution to identify abnormalities in its applicants’ chest X-rays, potentially modernizing a manual underwriting process and uncovering a new non-clinical market for AI vendors.
Lunit INSIGHT CXR will be integrated into Cathay’s underwriting workflow, with the goals of enhancing its radiologists’ accuracy and efficiency, while improving Cathay’s underwriting decisions.
Lunit and Cathay have reason to be optimistic about this endeavor, given that their initial proof of concept study found that INSIGHT CXR:
- Improved Cathay’s radiologists’ reading accuracy by 20%
- Reduced the radiologists’ overall reading time by up to 90%
Those improvements could have a significant labor impact, considering that Cathay’s rads review 30,000 CXRs every year. They might have an even greater business impact, noting the important role that underwriting accuracy has on policy profitability.
Lunit’s part of the announcement largely focused on its expansion beyond clinical settings, revealing plans to “become the driving force of digital innovation in the global insurance market” and to further expand its business into “various sectors outside the hospital setting.”
The Takeaway
Even if life insurers only require CXRs for a small percentage of their applicants (older people, higher value policies), they still review hundreds of thousands of CXRs each year. That makes insurers an intriguing new market segment for AI vendors, and makes you wonder what other non-clinical AI use cases might exist. However, it might also make radiologists who are still skeptical about AI concerned.
|




|
|
An Image Sharing Starting Point
Imaging providers who want to finally #ditchthedisk can now start off with Novarad’s CryptoChart Lite solution, a no-cost version of CryptoChart built for providers transitioning to imaging sharing.
|
|
A Fast and Reliable Second Opinion
See why radiologist Dr. Eleanna Saloura called Arterys’ Lung AI solution “a fast and reliable second opinion” for chest CT lung nodule analysis and tracking, allowing “more accurate diagnostic and treatment decisions.”
|
|
- MAGNETOM Free.Star’s FDA: Siemens Healthineers continued its accessibility-focused MRI lineup expansion, announcing the FDA clearance of its MAGNETOM Free.Star MRI system. The whole-body MRI inherits much of the previously-launched MAGNETOM Free.Max’s accessibility-focused qualities (0.55T, 60cm bore, very small/light, low helium & installation requirements), while leveraging its low energy and acquisition costs to become the company’s “most affordable MR system ever” (30% lower TCO than conventional MRs).
- No Doctor Required: The recent wave of autonomous AI approvals and studies inspired an excellent new blog from Dr. Lauren Oakden-Rayner, questioning whether AI can truly detect “normal” exams accurately enough to skip radiologist review. Dr. Oakden-Rayner argues that “narrow AI” tasks aren’t as narrow as we think (e.g. there are many types of fractures), while detecting “normal” exams would require extremely complex AI systems (training for all possible images, pathologies, etc.) that warrant far more rigorous testing. However, she sees the clinical benefits of adopting this kind of AI, as long as it’s subjected to the highest levels of scrutiny.
- TIA Imaging Overuse: Johns Hopkins researchers showed that neurovascular imaging (MRA & CTA) is overused for suspected transient ischemic attack (TIA), instead encouraging DWI MRI for TIA triage. Among 398 ED patients with transient neurologic deficits, 84% underwent neurovascular imaging and only 28% of these patients were diagnosed with TIA. MRA/CTA detected severe intracranial and cervical vessel stenosis in 10.5% and 1.7% of patients, although those rates were far higher among patients with positive DWI results (24.4% & 2.4%) and much lower with negative DWI scans (7.8% & 0.9%). Growing frustrations about CTA utilization made this study quite popular on rad Twitter.
- Unilabs’ SubtleMR Rollout: European diagnostics giant Unilabs announced its adoption of Subtle Medical’s SubtleMR deep learning MRI reconstruction solution, highlighting how SubtleMR’s scan time reductions will enhance its MRI operational efficiency and patient experiences. Unilabs will initially adopt SubtleMR across its Swedish locations before expanding the solution to its other European imaging centers. The alliance solidifies Subtle Medical’s presence among Europe’s largest imaging center companies following its longstanding partnership with EU imaging center giant, Affidea.
- BoneView’s Trauma Value: A new study out of France highlighted the accuracy and workflow advantages of GLEAMER’s BoneView X-ray fracture detection solution. Three radiologists interpreted 500 trauma patients’ X-rays with and without AI, finding that BoneView significantly improved the rads’ sensitivity (86% vs. 66%) and negative predictive value (92% vs. 82%), while maintaining specificity (+0.6% to 96%). BoneView also improved the senior radiologist, the rad fellow, and rad resident’s AUCs (0.938 vs. 0.832; 0.907 vs. 0.805; 0.891 vs. 0.792) and reduced their reading times per patient (-10, -16, -12 seconds).
- Developing a Helicopter CT: The Norwegian Air Ambulance Foundation and Airbus are developing CT-equipped helicopter ambulances to transport the country’s most rural stroke patients. The NAAF will work on sourcing a CT that’s small and light enough for helicopter operation, while Airbus will provide design and installation guidance. They plan to launch a test CT helicopter within the next four to five years.
- A Case for Dementia Precision Medicine: A new Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease study detailed an MRI-guided precision medicine approach that could help avoid or limit Alzheimer’s disease. The researchers evaluated 25 patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment for potential contributors (e.g. inflammation, nutrients, hormones, microbiomes, genetics, etc.) and then developed personalized treatment plans for each patient. After nine months of treatment, the patients showed significant improvements across most key metrics, including significant cognitive improvements among 84% of the patients, and increases in regional brain volumes (measured with MRI and Brainreader software).
- Aetna’s Cardiac PET/CT Reversal: Aetna reversed its cardiac PET/CT policy, and will cover the exams going forward. Aetna historically declined hybrid PET/CT for coronary artery disease evaluation, calling the exams “experimental/ investigational.” However, Aetna changed its policy following lobbying efforts from the SNMMI and ASNC who argued that cardiac PET/CT is accepted by medical associations and covered by CMS and other major payors.
- Fujifilm’s Portable R/F: Fujifilm announced the US launch of its unique FDR Cross portable fluoroscopy and digital radiography system. The FDR Cross features a dual-function c-arm (fluoro and X-ray at each end) and runs on battery power, reducing hospitals and ASCs’ need to use multiple imaging systems during image-guided procedures. The launch continues Fujifilm’s recent expansion into the R/F and surgical C-arm segments.
- 99mTc-Sestamibi for Renal Masses: A new JNM study highlighted 99mTc-Sestamibi SPECT/CT’s diagnostic advantage over contrast enhanced-CT for differentiating malignant and benign solid renal masses. The researchers reviewed imaging exams and pathology results from 27 patients who underwent 99mTc-Sestamibi SPECT/CT (20 also received CE-CT), finding that SPECT/CT diagnosed benign lesions with much higher sensitivity and specificity (66.7% & 89.5% vs. 10% & 75%) and correctly classified far more renal cell carcinoma lesions (80% vs. 33.3%).
- Rural Hospitals’ Radiology Requirement: In the wake of record closures of rural hospitals, CMS released the conditions of participation for the new Rural Emergency Hospital (REH) provider type that would enable them to take part in Medicare and Medicaid programs. The proposed rule requires REHs to provide emergency, laboratory, and radiologic services to meet the needs of patients in a manner consistent with Critical Access Hospitals, but adds more flexibility to staffing and outpatient services requirements.
|
|
Automating Echo AI
Check out this Imaging Wire Show featuring Us2.ai’s co-founders, James Hare and Carolyn Lam MBBS, PhD, detailing Us2.ai’s unique origins, impressive capabilities, and big goals to automate echocardiography reporting across the world.
|
|
- This Riverain Technologies case study details how Einstein Medical Center adopted ClearRead CT enterprise-wide (all 13 CT scanners) and how the solution allowed Einstein radiologists to identify small nodules faster and more reliably.
- See how Dubai-based healthcare leader Aster DM Healthcare leveraged the CARPL platform to connect its doctors, data scientists, and imaging workflows, and support its AI projects and development infrastructure.
- Working on your organization’s AI strategy? This Blackford Analysis post outlines the key considerations for creating your AI goals and strategy, including some you might not have considered.
- Clinicians are using the NAEOTOM Alpha to overcome limitations previously thought unavoidable in CT, with ultra-high spatial resolution without dose penalty and detailed spectral imaging without compromises. Get the facts about the technology and the benefits of photon-counting CT.
- The Hyperfine Swoop Portable MR’s accessibility advantages can translate to significant clinical and operational value, particularly for hospital emergency and intensive care departments. See how bringing MRI to the point-of-care can impact hospitals’ operational costs, quality of care, and revenue potential.
- Faced with two aging legacy PACS systems, South Jersey Radiology Associates moved to Intelerad’s IntelePACS, allowing its 12 sites to operate as a single, more-efficient entity. See how SJRA has since improved its radiologist efficiency by 8% to 10% and achieved a unified experience across its locations.
- Discover how Enlitic’s Curie|ENDEX application transforms medical imaging data to a standard nomenclature to form a foundation for successful artificial intelligence strategies.
|
|
|
|
|