|
Real AI Efficiency | Ditching the Disk
June 19, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“That is a slippery slope that I really want to ski down.”
|
|
University of Michigan health policy professor Dr. A. Mark Fendrick on his willingness to sacrifice coverage of low-value screenings in order to increase coverage of post-screening diagnostics.
|
|
|
|
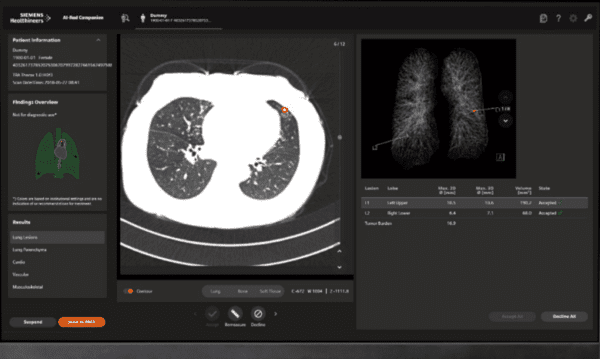
A new AJR study out of the Medical University of South Carolina showed that Siemens Healthineers’ AI-RAD Companion Chest CT solution significantly reduced radiologists’ interpretation times. Considering that radiologist efficiency is often sacrificed in order to achieve AI’s accuracy and prioritization benefits, this study is worth a deeper look.
MUSC integrated Siemens’ AI-RAD Companion Chest CT into their PACS workflow, providing its radiologists with automated image analysis, quantification, visualization, and results for several key chest CT exams.
Three cardiothoracic radiologists were randomly assigned chest CT exams from 390 patients (195 w/ AI support), finding that the average AI-supported interpretations were significantly faster. . .
- For the combined readers – 328 vs. 421 seconds
- For each individual radiologist – 289 vs. 344; 449 vs. 649; 281 vs. 348 seconds
- For contrast-enhanced scans – 20% faster
- For non-contrast scans – 24.2% faster
- For negative scans – 26.4% faster
- For positive scans without significant new findings – 25.7% faster
- For positive scans with significant new findings – 20.4% faster
Overall, the solution allowed a 22.1% average reduction in radiologist interpretation times, or an hour per typical workday.
The authors didn’t explore the solution’s impact on radiologist accuracy, noting that AI accuracy has already been covered in plenty of previous studies. In fact, members of this same MUSC research team previously showed that AI-RAD Companion Chest CT identified abnormalities more accurately than many of its radiologists.
The Takeaway
Out of the hundreds of AI studies we see each year, very few have tried to measure efficiency gains and even fewer have shown that AI actually reduces radiologist interpretation times.
Given the massive exam volumes that radiologists are facing and the crucial role efficiency plays in AI ROI calculations, these results are particularly encouraging, and suggest that AI can indeed improve both accuracy and efficiency.
|




|
|
COPC Ditches the Disk with Novarad
See how Novarad’s CryptoChart solution allowed Central Ohio Primary Care (COPC, 70 practices, 400 physicians) to make the transition to digital imaging sharing in this Healthcare IT News case study.
|
|
- The Cost of Follow-Ups: A recent KHN exposé brought attention to the downstream out-of-pocket costs created by the US’ policy of covering preventive care (e.g. cancer screening), but not follow-up diagnostics (biopsies, imaging, etc). The article highlighted recent progress with follow-up colonoscopies and CTCs, and ongoing legislative efforts to cover follow-up breast cancer diagnostics, but warned that these efforts will have to overcome pushback from payors.
- Aidoc’s $110M Expansion: Aidoc closed a massive $110M Series D round, increasing its total funding to $250M, and revealing plans to further expand its AI Care Platform across hospital departments. Nine-figure funding totals have historically been reserved for care-connected imaging AI players (e.g. Viz.ai’s $251M & HeartFlow’s $577M) or healthcare startups outside of radiology, so this is a major milestone for the triage/detection side of AI (where Aidoc got its start). Meanwhile, an expansion to new hospital service lines and clinical workflows would be a major step for Aidoc’s long-term strategy.
- O-RADS General Effectiveness: A recent JAMA study showed that the ACR Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting and Data Systems (O-RADS) ultrasound risk stratification system also performs well with low-risk populations. The study among non-selected, low-risk women (n = 913, w/ 1,014 adnexal lesions) found that O-RADS US 4 was the optimum cutoff for diagnosing cancer, with 90.6% sensitivity, 81.9% specificity, 31.4% PPV, and 99% NPV. Researchers have previously validated O-RADS in selected populations, but this research shows the system can also be applied to a general population of women seeking pelvic ultrasonography.
- YNHH Home Hospital: Yale New Haven Health is partnering with Medically Home to launch a Home Hospital Program for local Medicare patients. Patients who would otherwise need to be hospitalized will instead receive a daily telehealth visit with a physician through a provided tablet, twice-daily in-person visits from a nurse, plus additional services (including mobile imaging). Although this isn’t really an imaging story, patient care’s continued shift beyond hospital walls definitely has imaging implications.
- Cardiac MRI AI Measurements: UK researchers developed and evaluated a cardiac MRI AI model, finding that the model’s automated CMRI measurements correlated better than manual measurements for left ventricular stroke volume (r = 0.74 vs. 0.68), pulmonary vascular resistance (r = 0.62 vs. 0.41), and pulmonary artery pressure (r = 0.56 vs. 0.37) with 178 patients. Moreover, AI-measured right ventricular end-systolic volume, ejection fraction, and mass all predicted mortality in 920 patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (hazard ratios: 1.40, 0.76, and 1.15) over a 3.8yr average follow-up period.
- Hyperfine Down Under: Hyperfine announced that its Swoop portable MRI is now available in Australia and New Zealand, following the completion of its AU/NZ registration and notification process and the appointment of Quantum HealthCare as its local distributor. Multiple Swoop pilot research units have already been ordered across key Australia and New Zealand cities, laying the foundation for its upcoming commercial efforts.
- Refining Lung Cancer Screening Candidates: A new Radiology Journal paper detailed an AI-based approach for improving lung cancer screening candidate selection, compared to the current USPSTF criteria. The research showed that excluding low- or indeterminate- risk candidates (identified with CXR-based AI) from a subset of USPSTF-eligible individuals (n = 7,835) reduced the proportion of candidates selected for LD-CT screening from 45.1% to 35.8%, while maintaining cancer inclusion rates (0.3% vs. 0.3%) and PPV (0.9% vs. 0.7%; P=0.85).
- Infinitt & Brainreader: INFINITT North America announced plans to integrate Brainreader’s FDA-cleared Neuroreader software. Neuroreader can visualize and quantify 45 individual brain structures on MRIs in under 10 minutes, helping clinicians determine which regions are abnormal and to what extent.
- AI Model Imbalances: When AI models are trained on datasets weighted towards patients with the condition they’re trying to predict, they often struggle to identify patients without the condition. A new study published in JAMIA found that efforts to correct these imbalances frequently do more harm than good. In an ovarian cancer study, the authors found that adding more examples of the minority outcome to fix the model led to a strong overestimation of patients in the minority group, further adding to the miscalibration and reducing the model’s clinical viability.
- Another Call to Ditch the Disk: Former ACR Chair Geraldine McGinty, M.D., MBA, FACR took another stand against CD-based image sharing in a Journal of Digital Imaging editorial. Dr. McGinty outlined the “outdated” and “embarrassing” practice’s impact on repeat imaging volumes/costs, incidental findings, and diagnostic accuracy (due to lack of access to priors), calling for a multi-stakeholder effort and potential changes to regulations/reimbursements to address this issue. However, she admits that we might not be able to completely “Ditch the Disk” until using CDs becomes prohibited.
- Healthcare Hiring Boost: The US healthcare sector recently saw a bump in hiring according to the May Jobs Report, adding 28k jobs throughout last month, including 16k hospital workers. Following hospitals, the subsectors with the largest workforce gains were ambulatory services, physician offices, and nursing care facilities, each adding ~6k employees. Despite the improvement, the healthcare workforce remains 1.3% (223k jobs) below pre-pandemic levels, compared to a 0.5% decline across all industries.
|
|
Improving Accuracy and Scale with Cloud AI
See how AI and the cloud combine to alleviate IT challenges and amplify radiologist performance in this new Arterys white paper.
|
|
- Considering your short and long-term AI plan? Check out Canon Medical’s State of AI Roundtable, sharing insights into how imaging AI is being used, where it’s needed most, and how AI might assume a core role in medical imaging.
- Molecular imaging has played a critical role in oncology for decades, and the development of new radiopharmaceuticals and targeted therapeutics might prove to be crucial for achieving the promise of precision medicine. See how in this thought provoking GE Healthcare post.
- Adopting a platform strategy can simplify the deployment and management of imaging applications and AI algorithms, but there’s a lot to consider. In this eBook, Blackford Analysis and its clients detail how AI platforms can benefit clinical and IT teams, and share guidelines to consider when selecting a platform.
- This Riverain Technologies case study details how Einstein Medical Center adopted ClearRead CT enterprise-wide (all 13 CT scanners) and how the solution allowed Einstein radiologists to identify small nodules faster and more reliably.
- The Future of Radiology Starts on June 30th. Reserve your spot for AI Visions 2022, featuring live discussions from the top radiology and AI leaders and the global launch of Bayer’s Calantic Digital Solutions AI marketplace.
- Did you know one quarter of healthcare organizations have experienced a cyber-attack in the last year? This Change Healthcare animation explains how 3rd-party certified cloud-native enterprise imaging can help secure IT infrastructure that might be exposed with re-platformed imaging systems.
- Women’s imaging has come a long way, but operational efficiency remains a challenge for many facilities. To help address this challenge, this Fujifilm post details the five questions women’s imaging facilities should ask when evaluating workflow management solutions.
- Patients are ready for (and expecting) their healthcare to be supported by AI, and its gaining traction in radiology. See how AI is delivering clinical value today and in the future, in this editorial by Intelerad’s Morris Panner.
|
|
|
|
|