|
Autonomous & Ultrafast | MDR Non-Compliance
June 1, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“Well… in Mexico, 13th economy of the world, around 8-10k radiologists.. and we still print CTs and MRIs and write reports on Word which btw keeps changing half the medical words I write. 80% of hospitals don’t have open internet, I spend half my data on Radiopaedia, so yeah AI.”
|
|
Mexico-based radiologist Bernardo Medellin, adding some global context to estimates that 30% of radiologists are using AI.
|
|
|
|
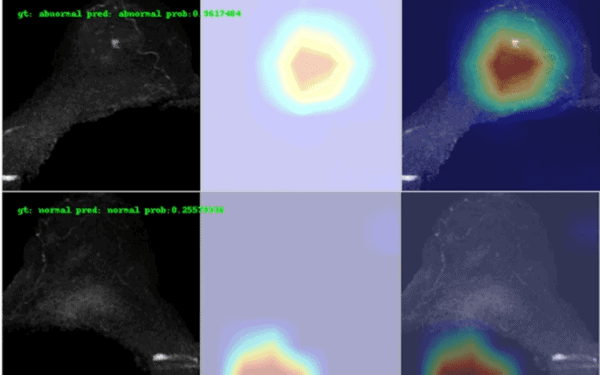
A new study out of the University of Groningen highlighted the scanning and diagnostic efficiency advantages that might come from combining ultrafast breast MRI with autonomous AI. That might make some readers uncomfortable, but the fact that autonomous AI is one of 2022’s most controversial topics makes this study worth some extra attention.
The researchers used 837 “TWIST” ultrafast breast MRI exams from 488 patients (118 abnormal breasts, 34 w/ malignant lesions) to train and validate a deep learning model to detect and automatically exclude normal exams from radiologist workloads. They then tested it against 178 exams from 149 patients from the same institution (55 abnormal, 30 w/ malignant lesions), achieving a 0.81 AUC.
When evaluated at a conservative 0.25 detection error threshold, the DL model:
- Achieved 98% sensitivity and negative predictive values
- Misclassified one abnormal exam as normal (out of 55)
- Correctly classified all exams with malignant lesions
- Would have reduced radiologists’ exam workload by 6.2% (-15.7% at breast level)
When evaluated at a 0.37 detection error threshold, the model:
- Achieved 95% sensitivity and a 97% negative predictive value (still high)
- Misclassified three abnormal exams (3 of 55), including one malignant lesion
- Would have reduced radiologists’ exam workload by 15.7% (-30.6% at breast level)
These radiologist workflow improvements would complement the TWIST ultrafast MRI sequence’s far shorter magnet time than current protocols (2 vs. 20 minutes), while the DL model could further reduce scan times by automatically ending exams once they are flagged as normal.
The Takeaway
Even if the world might not be ready for this type of autonomous AI workflow, this study is a good example of how abbreviated MRI protocols and AI could be able to improve both imaging team and radiologist efficiency. It’s also the latest in a series of studies exploring how AI could exclude normal scans from radiologist workflows, suggesting that the development and design of this type of autonomous AI will continue to mature.
|




|
|
Automating Echo AI
Check out this Imaging Wire Show featuring Us2.ai’s co-founders, James Hare and Carolyn Lam MBBS, PhD, detailing Us2.ai’s unique origins, impressive capabilities, and big goals to automate echocardiography reporting across the world.
|
|
Take the Canon AiCE Challenge
Take the AiCE challenge and see why half the radiologists in a recent study “had difficulty differentiating” images from Canon Medical Systems’ Vantage Orian 1.5T MR using its AiCE reconstruction technology compared to standard 3T MRI images.
|
|
- MDR Non-Compliance: AI for Radiology reports that only 33 of 198 (17%) CE-marked imaging AI products have been recertified under Europe’s year-old Medical Device Regulation requirements (MDR). The EU gave radiology AI software that was already on the market a three-year grace period to meet the more rigorous MDR requirements, although at the current rate, half of those products will not comply on time.
- SWE for Pediatric Liver Stiffness: A study out of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital showed that ultrasound shear-wave elastography is comparable to MR elastography for assessing liver shear stiffness in pediatric patients. Using MR elastography as the reference, the authors analyzed images from 44 children and young adults with known or suspected liver disease, finding that US SWE detected abnormal liver stiffness with a 0.95 AUC.
- BC Lung Cancer Screening: British Columbia is launching the province’s first lung cancer screening program, revealing plans to screen 10k high-risk patients and catch 150 early-stage cancer cases in its first year. The program will operate through 36 imaging centers, screening participants between 55 and 74 years-old with a smoking history of at least 20 years.
- Healthcare Worker Breaches: Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report revealed that employees are responsible for 39% of healthcare data breaches, more than double the 18% average across all industries. The findings show that most insider breaches are tied to unintentional errors as opposed to malicious misuse, with employees being 2.5 times more likely to make an error leading to a breach (e.g. send an email to the wrong address, lose a document) than purposefully abusing their access privileges.
- Osteoporosis Radiomics: A team of Korea-based researchers developed a deep-radiomics (DR) model that successfully detects osteoporosis in hip radiographs. When tested against an external dataset of 444 X-rays, their highest performing DR model outshined six radiologists (AUCs: 0.95 vs. 0.77) and significantly improved the radiologists’ performance when they had DR support (AUCs: 0.87 vs. 0.77).
- Patients’ AI Perspectives: An Intelerad survey of over 1,000 healthcare consumers suggests that the general public is far more optimistic about diagnostic AI than radiologists. The majority of respondents “either trust or are neutral” about autonomous AI-only diagnoses (64%) or radiologists using AI to support their diagnoses (79%), and they are even more open to non-diagnostic AI tasks like making appointments or prioritizing radiologists’ worklist (88% & 86%). They also have big expectations for AI, as 60% think that AI will perform over half of radiology services in five years, with that number increasing to 75% in the next 20 years.
- UPenn’s ARK: UPenn’s ultrasound research lab will utilize PaxeraHealth’s ARK platform, which allows users to develop their own AI algorithms without extensive coding. UPenn plans to use ARK to build its own ultrasound AI models designed to detect liver cancer and evaluate COVID severity, and expects that ARK will reduce the time to bring its AI models to market.
- Low on Helium: The dwindling helium supply hit mainstream news last week following the Dollar Tree publicizing concern that the helium deficit will impact its graduation and birthday balloon sales. MRI users and vendors are well aware of the helium shortage, but this may still be a good conversation starter for MRI players with a strong low-helium value proposition.
- Novarad Adds CryptoChart Lite: Novarad expanded its imaging sharing portfolio with the launch of its CryptoChart Lite solution. CryptoChart Lite is a no-cost version of Novarad’s established CryptoChart solution, similarly leveraging a printed encrypted QR code or web access code to support image storage and transfer (no CDs, logins, portals, or software installs). Although providers would have to upgrade to the full CryptoChart version to access more advanced features, CryptoChart Lite should serve as a useful starting point for those who are becoming ready to ditch the disk.
- Move Slow and Test Things: Google AI’s principal research director Greg Corrado recently spoke at STAT’s Health Tech Summit about his plans to address concerns surrounding healthcare AI. Corrado said that Facebook’s infamous “move fast and break things” slogan is the exact opposite of how tech companies should approach health AI problems, and listed several considerations such as performing rigorous testing at each step of algorithm development and ensuring that models are tested with data from populations where they’ll be used.
- DLR Supports CT-FFR: A new study out of China found that deep learning image reconstruction (DLR) improves coronary CTA image quality, and more importantly, doesn’t negatively impact CT-FFR diagnostic performance. Using QFR and invasive FFR results as a reference, the authors analyzed DLR and four other reconstruction approaches using 182 CTAs from 33 patients, finding no significant difference across their CT-FFR values and diagnostic performance (AUCs: 0.83 vs. 0.81 to 0.86; p>0.05).
|
|
Riverain’s MDR Certification
Riverain is part of the exclusive group of AI vendors to receive Europe’s more-demanding Medical Device Regulations (MDR) certification, which as you read above, requires healthcare AI products to attain higher risk classifications and provide far more validation evidence.
|
|
- Precision medicine startup BAMF Health just installed United Imaging’s uEXPLORER scanner, making it the first total-body PET/CT used for theranostics in the US. See how this combination will allow BAMF Health to deliver more effective and efficient theranostics treatments.
- Catch the Intelerad team at SIIM 2022 next week, where they’ll be participating in panels discussing the cloud, data anonymization, and diversity, equity, and inclusion (including Intelerad’s partners from RADequal – formerly RADxx).
- Reserve your spot for AI Visions 2022, featuring live discussions from the top radiology and AI leaders and the global launch of Bayer’s Calantic Digital Solutions AI marketplace.
- See how Novarad’s CryptoChart solution allowed Central Ohio Primary Care (COPC, 70 practices, 400 physicians) to make the transition to digital imaging sharing in this Healthcare IT News case study.
- The flow of new AI applications makes it hard for radiology groups to determine which tools would help them and how IT teams can handle increased AI adoption. In this Blackford Analysis white paper, radiology and IT leaders from NYU and Canopy Partners share how a platform approach alongside a curated marketplace can help solve these challenges.
- When Sao Paolo’s Diagnosticos da America SA (DASA, the world’s 4th largest diagnostics company) set out to evaluate Qure.ai’s QXR solution for their pediatric chest X-ray workflows, they leveraged CARPL.ai’s platform to streamline their evaluation. See how it worked here.
- See how Fujifilm Healthcare helped Arkansas Children’s Hospital imaging IT infrastructure evolve from departmental silos to an interoperable architecture that improved its radiology and IT teams’ day-to-day flexibility and future scalability.
- Watch Einstein Healthcare’s Terry Matalon, MD, describe how combining Nuance PowerScribe One with the Nuance AI Marketplace’s workflow integrated AI improved their radiology reporting accuracy and confidence.
- Symbia SPECT/CT has a great history, and there is more to come. Be among the first to see how Siemens Healthineers’ Symbia SPECT/CT is taking major steps in patient access, ease of use, and clinical versatility at their virtual launch event on June 9th.
|
|
|
|
|