|
Echo Automation | LVO AI Reminder
April 13, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“No one will win the Nobel Prize in medicine for applying AI to health care administration. “
|
|
A recent MIT Sloan editorial noting one of the few downsides to administrative AI.
|
|
|
|
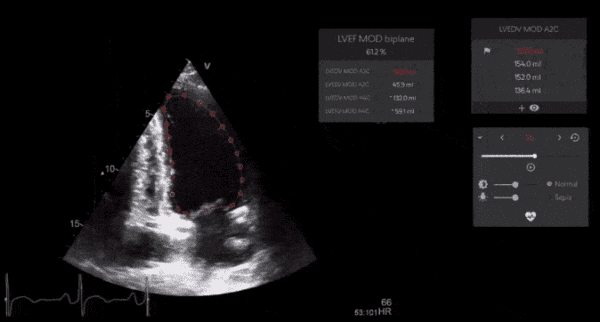
One of imaging AI’s hottest segments just got even hotter with the completion of Us2.ai’s $15M Series A round and the global launch of its flagship echocardiography AI solution. It’s been at least a year since we led-off a newsletter with a funding announcement, but Us2.ai’s unique foundation and the echo AI segment’s rapid evolution makes this a story worth telling…
Us2.ai has already achieved FDA clearance, a growing list of clinical evidence, and key hardware and pharma alliances (EchoNous & AstraZeneca).
- The Singapore-based startup also has a unique level of credibility, including co-founders with a history of clinical and business success, and VC support from IHH Healthcare (the world’s second largest health system).
- With its funding secured, Us2.ai will accelerate its commercial and regulatory expansion, with a focus on driving global clinical adoption (US, Europe, and Asia) and developing new alliances (hardware vendors, healthcare providers, researchers, pharma).
Us2.ai joins a crowded echo AI arena, which might have more commercial-stage vendors than all other ultrasound AI segments combined. In fact, the major echo guidance (Caption Health, UltraSight) and echo reporting (DiA Imaging, Ultromics, Us2.ai) AI startups have already generated more than $180M in combined VC funding and forged a number of major hardware and PACS partnerships.
- This influx of echo AI startups might be warranted, given echocardiography’s workforce, efficiency, and variability challenges. It might even prove to be visionary if handheld ultrasounds continue their rapid expansion to new users and settings (including primary and at-home care).
- Us2.ai will have to rely on its reporting advantages to stand out against its well-established competitors, as it is the only vendor to completely automate echo reporting (complete editable/explainable reports in 2 minutes) and analyze every chamber of the heart (vs. just left ventricle with some vendors).
- That said, the incumbent echo AI players have big head starts and the impact of Us2.ai’s automation advantage will rely on ultrasound OEMs’ openness to new alliances and (of course) the rate that providers embrace AI for echo reporting.
The Takeaway
Even if many cardiologists and sonographers would have a hard time differentiating the various echo AI solutions, this is a segment that’s showing a high level of product-market fit. That’s more than you can say for most imaging AI segments, and product advancements like Us2.ai’s should improve this alignment. It might even help drive widespread adoption.
|




|
|
Take the Canon AiCE Challenge
Take the AiCE challenge and see why half the radiologists in a recent study “had difficulty differentiating” images from Canon Medical Systems’ Vantage Orian 1.5T MR using its AiCE reconstruction technology compared to standard 3T MRI images.
|
|
Duke’s Case for ClearRead CT
This Riverain Technologies case study details how Duke University Medical Center integrated ClearRead CT into its chest CT workflows, reducing read times by 26% and improving nodule detection by 29%.
|
|
- MRI Scan-a-Van: Researchers from Brown University and Hyperfine developed a proof-of-concept mobile MRI by installing a Hyperfine Swoop low-field MRI in a modified cargo van. After finding that their “Scan-a-Van” might be able to perform quick and accurate point-of-patient brain MRI exams (e.g. at patient homes or assisted living facilities), the authors suggested that this approach might improve imaging access for patients unable to travel to imaging centers or hospitals (e.g. mobility challenges, rural locations). The study also comes just a few months after MUSC Health similarly debuted the first stroke ambulance mobile MRI.
- FDA LVO AI Reminder: The US FDA published a “reminder” that AI-based LVO (CADt) detection tools are intended to triage and prioritize suspected large vessel occlusion cases, not provide diagnostic information or eliminate cases from radiologists’ worklists. That might seem like an unnecessary reminder, but this is actually a strong message from the FDA (who rarely publishes these reminders) that clinicians should not take clinical action based on CADt output alone. Considering the growing role of CADt care coordination tools that deliver their output via smartphones to non-rad clinicians, there are plenty of opportunities for clinicians to misunderstand CADt’s intended use case and act without confirming radiologists’ interpretations.
- Developing a PET Supplement: A Memorial Sloan Kettering-led team developed a Cerenkov light imaging (CLI) technique that could evolve into a PET supplement for patients in low-resource settings. The researchers performed CLI on 96 patients with existing or suspected tumors, finding that the technique localized tumors with ‘acceptable’ or higher agreement with PET exams among 90% of the patients. The researchers aren’t looking to replace PET, but CLI’s speed and cost benefits could make it a viable PET supplement for smaller/rural providers without an on-site PET system or in countries without nearly enough PET scanners.
- Arterys’ Neuro AI Expansion: Arterys continued its Neuro AI platform expansion, officially launching its Combinostics-based cNeuro cMRI solution, which automates white matter lesion quantification to support multiple sclerosis and dementia assessments. cNeuro joins a growing list of solutions on the Neuro AI platform, which also includes LVO/ ICH stroke detection, 4D Flow, and tumor diagnostics tools.
- De-innovation: Becker’s published an interesting article exploring Cleveland Clinic and other organizations’ “de-innovation” processes for discontinuing practices that no longer benefit the health systems. The piece included recommendations such as ensuring that “data from the legacy applications is archived and the technology is sunset” and that “hospitals should apply the same enthusiasm they have when launching new projects to asking the hard questions about which operations might need to be eliminated.” The article didn’t mention radiology, but we’re sure some readers can think of imaging processes that belong on their de-innovation list.
- Emory Adds Fujifilm Cardiology PACS: Fujifilm Healthcare installed its 7x Synapse Cardiology PACS across Emory Healthcare, including the Georgia system’s 11 hospitals and 23 heart and vascular clinics. The installation comes just a year after Sectra announced an enterprise imaging deal supporting Emory’s radiology and orthopedics departments.
- RP Takes the Stand: The federal criminal conspiracy case against DaVita and its CEO named Radiology Partners among the three companies that allegedly had anti-poaching agreements with the dialysis giant. RP seems to have played a smaller role, which is so far limited to an informal “ground rules” email after RP already hired several DaVita execs. That said, this is a high-profile antitrust case with major healthcare labor implications, and RP’s hiring practices might be subject to more public scrutiny as the trial continues.
- All in on Admin AI: Clinical AI might get all the headlines, but a recent MIT Sloan Management Review editorial stated a compelling case for why “administrative AI may be a better bet.” The authors detailed clinical AI’s long list of adoption and ROI barriers (regulatory approval, physician acceptance, workflow integration, reimbursements, inefficiency), arguing that admin AI solutions avoid many of these barriers and target problems that are far more solvable and more likely to deliver economic ROI. After all, administrative tasks are responsible for 34% of US healthcare costs and probably an even higher share of healthcare waste.
- Surveillance Mammography Declines: A new JNCCN study revealed significant declines in surveillance mammography adherence since 2009. Analysis of 142k commercially insured breast cancer survivors (aged 40-64yrs) showed that annual surveillance mammography use declined by 1.5% annually from 2009 to 2016 (73.7% to 67.1%) after remaining stable from 2004 to 2009 (~74%). These declines occurred across healthcare and demographic segments, although they were greatest among younger women (40-49yrs fell by 2.8%/yr after 2009) and women with lower deductibles (-2,1%/yr after 2010).
- Encord’s Auto-Annotation Launch: Computer vision startup Encord announced the launch of its CordVision DICOM image annotation solution, which uses deep learning to automate manual labeling processes. AI development teams would label a small/representative set of images that are used to train CordVision to automatically label a much larger database – and that data would be used to train AI models. Equipped with $17M in 2021 VC funding, Encord joins a growing group of startups targeting the “picks and shovels” side of AI, alongside labeling competitors like Centaur Labs and Gradient Health, as well as AI validation companies like Gesund and CARPL.ai.
- Hospital M&A Slowdown: Only 12 US hospital acquisitions were announced in Q1 2022, the lowest total since Kaufman Hall began tracking the metric in 2016. On top of the low total, there were no mega transactions where the acquisition target had revenues over $1B, driving down the average revenue of the acquired hospital to $246M (vs. $619M in 2021). Kaufman Hall referred to the Q1 results as “an interesting anomaly,” and expects activity to pick back up given the clear benefits of health system scale.
|
|
AI’s Barriers and Benefits
We hear a lot about AI being the next big thing or being immature and overhyped. This set of Blackford Analysis editorials reviews the challenges that are still holding back imaging AI, and the areas that AI is delivering genuine clinical benefits.
|
|
- Change Healthcare’s cloud-native, zero-footprint Stratus Imaging PACS is now live in clinical use. See how Stratus Imaging PACS is helping radiology practices improve productivity and patient care, while eliminating the cost and resource constraints of on-premise systems.
- United Imaging’s uCT ATLAS ultra-premium CT scanner delivers imaging that covers it all. That means 16 cm whole organ coverage, enabling a non-contrast brain in a half-second with a single rotation. That also means whole-heart coverage combined with 0.25 second rotation speed, providing high-quality and low-dose images within one heartbeat.
- How can artificial intelligence (AI) help improve clinical and operational performance in MRI? Listen to the latest Siemens Healthineers podcast to learn more.
- Do your radiologists want faster and less manual access to imaging studies? See how the Indiana Health Information Exchange (IHIE), the largest inter-organizational clinical data repository in the US, cut its imaging study retrieval time by 94% when it adopted Nuance PowerShare.
- This American College of Cardiology case report details how Arterys’ 4D flow enhances visualization of blood flow and pulmonary venous anatomy in cardiac MRI, improving diagnosis and surgical planning for partial anomalous pulmonary venous return.
- With radiologist workloads growing in volume and complexity, having the wrong PACS can lead to radiologist burnout. This helpful Fujifilm post shows how having the right PACS that functions as a centralized and integrated enterprise imaging system can be part of the solution.
- With its sleek and compact design, GE Healthcare’s LOGIQ Fortis can be used in almost any space, and its features and technologies make it strong enough to conduct a full spectrum of ultrasound exams and procedures on any body type.
- CD burning issues? Check out this one-minute video showing how Novarad’s CryptoChart image sharing solution allows patients to easily access and share their medical images using personalized, highly secure QR codes (not CDs).
- Us2.ai’s echocardiography analysis automation solution is being integrated into the EchoNous Kosmos ultrasound platform, creating the most powerful diagnostic “power tool” ever created for the hand-carried POCUS market.
- See how Dubai-based healthcare leader Aster DM Healthcare leveraged the CARPL platform to connect its doctors, data scientists, and imaging workflows, and support its AI projects and development infrastructure.
|
|
|
|
|