|
Autonomous AI Approval | Outpatient Shift
March 30, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“Nothing helps more with the wellness of radiology attendings than smart, hard working, competent trainees. Not even meditation. Or wellness questionnaires.”
|
|
A Tweet from Penn Medicine radiologist and appreciator of good trainees, Saurabh Jha, MD.
|
|
|
|
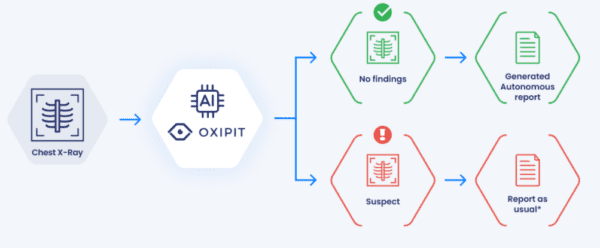
Just as the debate over whether AI might replace radiologists is starting to fade away, Oxipit’s ChestLink solution became the first regulatory-approved imaging AI product intended to perform diagnoses without involving radiologists (*please see editor’s note below regarding Behold.ai). That’s a big and potentially controversial milestone in the evolution of imaging AI and it’s worth a deeper look.
About ChestLink – ChestLink autonomously identifies CXRs without abnormalities and produces final reports for each of these “normal” exams, automating 15% to 40% of reporting workflows.
Automation Evidence – Oxipit has already piloted ChestLink in supervised settings for over a year, processing over 500k real-world CXRs with 99% sensitivity and no clinically relevant errors.
The Rollout – With its CE Class IIb Mark finalized, Oxipit is now planning to roll out ChestLink across Europe and begin “fully autonomous” operation by early 2023. Oxipit specifically mentioned primary care settings (many normal CXRs) and large-scale screening projects (high volumes, many normal scans) in its announcement, but ChestLink doesn’t appear limited to those use cases.
ChestLink’s ability to address radiologist shortages and reduce labor costs seem like strong and unique advantages. However, radiology’s first regulatory approved autonomous AI solution might face even stronger challenges:
- ChestLink’s CE Mark doesn’t account for country-specific regulations around autonomous diagnostic reporting (e.g. the UK requires “appropriate reporting” with ionizing radiation-based exams)
- Radiologist societies historically push back against anything that might undermine radiologists’ clinical roles, earning potential, and future career stability
- Health systems’ evidence requirements for any autonomous AI tools would likely be extremely high, and they might expect similarly high economic ROI in order to justify the associated diagnostic or reputational risks
- Even the comments in Oxipit’s LinkedIn announcement had a much more skeptical tone than we typically see with regulatory approval announcements
The Takeaway
Autonomous AI products like ChestLink could address some of radiology’s greatest problems (radiologist overwork, staffing shortages, volume growth, low access in developing countries) and their economic value proposition is far stronger than most other diagnostic AI products.
However, autonomous AI solutions could also face more obstacles than any other imaging AI products we’ve seen so far, suggesting that it would take a combination of excellent clinical performance and major changes in healthcare policies/philosophies in order for autonomous AI to reach mainstream adoption.
*Editor’s Note – April 21, 2022: Behold.ai insists that it is the first imaging AI company to receive regulatory approval for autonomous AI. Its product is used with radiologist involvement and local UK guidelines require that radiologists read exams that use ionizing radiation. All above analysis regarding the possibilities and challenges of autonomous AI applies to any autonomous AI vendor in the current AI environment, including both Oxipit and Behold.ai.
|




|
|
Ramapo Radiology’s Case for Novarad CryptoChart
See how New Jersey’s Ramapo Radiology Associates overcame their CD burning problems and improved their physician and patient experiences with Novarad CryptoChart.
|
|
Us2.ai and EchoNous Integrate
Us2.ai’s echocardiography analysis automation solution is being integrated into the EchoNous Kosmos ultrasound platform, creating the most powerful diagnostic “power tool” ever created for the hand-carried POCUS market.
|
|
- Inpatient Care’s Decline: A new Moody’s report suggests that the pandemic accelerated the decline of inpatient care, with hospital outpatient revenue exceeding inpatient revenue every year since 2016. The firm predicts this trend will continue gaining momentum in the face of reimbursement changes and the rise of virtual care, pressuring systems that don’t have strong home care programs, while directing more inpatient demand towards hospitals that specialize in complex care.
- Transpara’s Detection Promise: A new study out of Norway highlighted ScreenPoint Transpara’s “promising” performance detecting cancer in mammography screening exams. The researchers used Transpara to analyze 122,969 screening mammograms from 47,877 women (w/ 752 screen-detected cancers, 205 interval cancers), and compared its results to radiologists’ double-reading interpretations and final outcomes. Transpara assigned its highest risk score (10 out of 10) to 86.8% of the screen-detected cancers and 44.9% of the interval cancers, while only 0.7% of screen-detected cancers were assigned its lowest risk score (1 out of 10).
- FDG PET/CT’s SBRT Predictions: A new Lancet study highlighted FDG PET/CT’s ability to accurately predict stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) treatment outcomes among patients with inoperable early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. The Brazil-based research team analyzed data from 47 patients who underwent SBRT, finding that none of the 19 patients with low FDG-PET/CT SUVmax values (≤ 5) experienced treatment failures (recurrence or metastasis), while 10 of the 28 patients with high FDG-PET/CT SUVmax values (≥ 5) experienced treatment failures.
- Qure.ai Funded: Qure.ai completed a $40M funding round (total now $56M not including Fractal’s startup funding) that it will use to support further expansion into the US and Europe and to intensify its product development efforts. This is one of the bigger AI funding rounds we’ve seen in the last year, and Qure.ai certainly earned it after building one of the broader AI portfolios and establishing itself as imaging AI’s TB and developing world leader. That also makes Qure.ai’s increased focus on western regions worth keeping an eye on.
- Paracentesis & Thoracentesis Shifts: A UPMC-led study of 2012-2018 Medicare data revealed major increases in image-guided paracentesis (171k to 253k) and image-guided thoracentesis (187k to 222k) procedure volumes, while blind paracentesis and thoracentesis volumes declined (17k to 12k; 26.7k to 15k). Although radiologists’ overall image-guided paracentesis / thoracentesis volumes increased, their share of these procedures actually declined (83.9% to 77.1%; 73.6% to 66.2%) due in part to a shift towards Advanced Practice Providers (10.2% to 15.8%; 7.7% to 12.9%).
- Aidoc’s Pneumothorax FDA: Aidoc announced the FDA 510(k) clearance of its new pneumothorax triage and notification solution, marking the company’s 8th FDA-cleared AI product and its first to analyze X-ray exams (all others analyze CT/CTA/CTPA). Aidoc joins a long list of AI vendors with pneumothorax solutions, but should be able to rely on its integrated triage platform and large user base to stand out in the pneumothorax AI crowd.
- Fewer False Positives with DBT: A new JAMA study showed that DBT is less likely to produce false positive breast cancer screening results than digital mammography, although false positives remain high with both methods. The large-scale study (903k women, 2.96M exams, 2005-2018 period) revealed that women screened with DBT had lower 10-year probabilities of receiving at least one false positive recall whether they participate in annual (49.6% vs. 56.3%) or biennial screenings (35.7% vs 38.1%). DBT also had lower 10-year risks of short-interval follow-up recommendations (annual: 16.6% vs 17.8%; biennial: 10.3% vs 10.5%) and biopsy recommendations (annual: 11.2% vs 11.7%; biennial: 6.6% vs 6.7%).
- US Health Spending Flattens: Despite increased patient care demand, CMS’ 2021-2030 National Health Expenditure report revealed that national health spending growth slowed to 4.2% in 2021 (vs. 9.7% in 2020) due in part to a drop in COVID-related federal aid. CMS forecasts national health spending to increase by 5.1% annually through 2030 when it will reach nearly $6.8 trillion. Given expected US GDP growth, healthcare’s share of GDP should remain relatively steady (19.7% in 2020 vs. 19.6% in 2030).
- ConcertAI’s $150M: TeraRecon’s parent company, ConcertAI, completed a massive $150M funding round, increasing its total funding to $300M and pushing its valuation to $1.9B. The announcement made it quite clear that ConcertAI’s strategy and hefty valuation are mainly tied to its life sciences and biopharma business (not specifically diagnostic imaging). That said, ConcertAI previously revealed plans to integrate TeraRecon’s imaging solutions into its core research/trial platform, so it’s likely that some of this funding will support this integration strategy.
- The DBT Mandate Effect: A new JAMA study revealed that statewide mandates requiring DBT mammography screening coverage increase DBT utilization, and decrease the overall cost of DBT exams, but don’t significantly impact costs to patients. Using Blue Cross Blue Shield data (n = 9.6M screenings, 5.7M women, 2015 and 2019) the study showed that statewide mandates increased DBT utilization by an average of 9 percentage points within the first two years, while overall exam costs fell by an average of $38.70 and patient OOP costs fell by just $2.10 (some states increased).
- Addressing Societal Bias: A recent report from the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) proposed expanding our list of AI bias sources to include broader societal factors that influence how AI tools are developed and used. The NIST encouraged a “socio-technical” approach to combating AI bias that would expand AI stakeholders well beyond the current technology and data-focused groups. The new NIST guidance is intended to address all kinds of AI use cases (e.g. hiring, education, criminal justice), but their recommendation certainly applies to healthcare.
|
|
A Case for GE Healthcare CMRI + AI Treatment Planning
See how one hospital combined GE Healthcare’s cardiac MRI scanners and AI technology to improve cardiac assessments and treatment planning.
|
|
- Check out this Imaging Wire Show, featuring Nanox AI strategy leader, Dr. Orit Wimpfheimer, where we discuss building an international telerad practice, what’s wrong with triage AI, and pivoting to population health AI.
- Enterprise Imaging has come a long way, and it has a long way to go. This Intelerad white paper details the five pillars organizations should prioritize in order to realize the full potential of EI’s next evolution.
- Variable heart rates and organ motion can make cardiac imaging a challenge for CT technologists. Discover how intelligent imaging guidance with Siemens Healthineers’ myExam Companion can help overcome these challenges, without compromising quality and consistency.
- This Riverain Technologies case study details how Duke University Medical Center integrated ClearRead CT into its chest CT workflows, reducing read times by 26% and improving nodule detection by 29%.
- Associated Urologists of North Carolina just became the latest home of one of United Imaging’s uCT 530 CT systems. See why Associated Urologists’ Cary, NC office called United Imaging’s CT team “the best.”
- See how Fujifilm Healthcare helped Arkansas Children’s Hospital imaging IT infrastructure evolve from departmental silos to an interoperable architecture that improved its radiology and IT teams’ day-to-day flexibility and future scalability.
- Check out this editorial by Nuance EVP Peter Durlach on how AI-augmented diagnostic imaging is driving new approaches to collaborative, patient-specific precision care.
- Did you know one quarter of healthcare organizations have experienced a cyber-attack in the last year? This Change Healthcare animation explains how 3rd-party certified cloud-native enterprise imaging can help secure IT infrastructure that might be exposed with re-platformed imaging systems.
- Canon’s Cartesion Prime is the only air-cooled digital PET/CT system, which means big reductions in service, chiller, and infrastructure costs. Check out Canon’s case for the air-cooled Cartesion Prime.
|
|
|
|
|