|
Fixing AI’s Drift Problem | Predicting RA
February 16, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“And drift, like FAMILY, is something you should never turn your back on.”
|
|
A tweet from Matthew Lungren, MD about AI’s post-deployment drift problem… and about family loyalty.
|
|
|
The Imaging Wire will return on Tuesday, February 22nd after a Monday hiatus for President’s Day. Enjoy the long weekend, and if you’ll miss having us in your inbox on Monday, consider forwarding this to your friends and colleagues to help them get up to speed on radiology news when we get back next week.
|
|
|
|
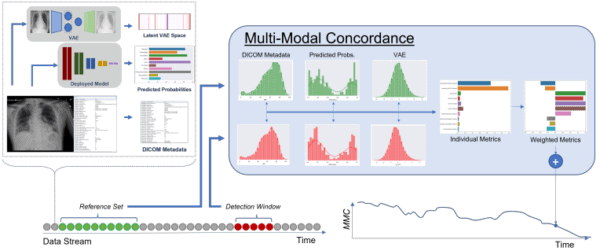
A Stanford AIMI and Microsoft Healthcare team just took a step towards addressing imaging AI’s looming drift problem, unveiling their CheXstray drift detection system.
Imaging AI’s Drift Problem – The list of FDA-cleared imaging AI products continues to grow and we’re getting better at AI deployment. However, there’s no reasonable way to monitor how imaging AI models adapt to their constantly changing data environments (tech, vendors, protocols, patient & disease mix, etc.) or whether the models change on their own.
The CheXstray Solution – The team used a pair of public CXR datasets (n = 224k & 160k CXRs) to train/test the CheXstray solution to automatically detect drift by calculating a range of multi-modal inputs (DICOM metadata, image appearance, clinical workflows) and model performance.
CheXstray Results – Initial experiments showed that the automated CheXstray workflows rivaled ground truth audits for drift detection, essentially achieving the workflow’s proof-of-concept goal.
Automation Alternatives – Until we have automated monitoring solutions like CheXstray, AI vendors and radiology departments might have to rely on ongoing audits (requiring test set curation, labeling, analytics, etc.) and/or asking radiologists to provide ongoing model feedback. Unfortunately, those options undermine AI’s intended labor-reducing value proposition. Plus, radiologists have already made it quite clear that they don’t think monitoring should be their responsibility (and regulators might agree).
The Takeaway
We haven’t solved imaging AI’s drift monitoring problem yet, and there will be other hurdles to overcome before we see a solution like this achieve clinical adoption (more research, regulatory changes, new modalities, training without massive public datasets). Still, the CheXstray team just showed how imaging AI performance could be automatically monitored in real-time. That’s an important step in imaging AI’s evolution, and it might prove to be critical as more hospitals head into the 2nd or 3rd years after their “successful” AI deployments.
|




|
|
Pivoting to Population Health AI
Check out this Imaging Wire Show, featuring Nanox AI strategy leader, Dr. Orit Wimpfheimer, where we discuss building an international telerad practice, what’s wrong with triage AI, and pivoting to population health AI.
|
|
Making PET/CT Accessible
Thinking about adding PET/CT to your clinical offerings but don’t have the patient volume to support a full-time scanner? Check out Siemens Healthineers’ fleet of Biograph mobile PET/CT solutions to learn how we can provide reliable, high-quality imaging with a focus on the patient experience – no matter the location.
|
|
- PET RA Predictions: A new study out of the Netherlands suggests that PET imaging might improve rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment response monitoring, identifying changes in RA-related immune cells earlier than current imaging methods (CT, MRI, US). The researchers performed whole-body macrophage PET/CT on 35 patients with early-stage RA who were beginning COBRA therapy, identifying notable PET uptake changes during week-two of the 13-week regiment (171 PET-positive joints at baseline, 100 joints at 2 weeks). Notably, they found that measuring PET uptake in the foot joints (highest uptake at baseline, greatest decreases at week 2) along with traditional DAS44 scoring might be sufficient for predicting treatment response, making whole-body exams unnecessary.
- HeartFlow SPAC Canceled: HeartFlow and Longview Acquisition Corp terminated their plans to go public via a reverse SPAC merger. The companies announced their SPAC merger last summer, which would have given HeartFlow a $2.4B enterprise value and $400M in the bank, but it appears that SPAC and medtech stock headwinds might have dissuaded them. Longview has reason to be cautious, noting that Butterfly Network (it’s previous SPAC merger) has seen its stock tumble 77% in the last year (~$26 to ~$6).
- More Transfer Learning Evidence: A new MGH and Ohio State study shared more evidence of transfer learning’s potential to improve AI generalizability and reduce image labeling work. The researchers trained an AI model to detect decreased ejection fraction and left ventricular hypertrophy using 4D cardiac CTA scans from “site 1,” and tested model performance using 45 CCTA scans from “site 2” before and after transfer learning. As you might expect, the transfer learning-based model had fewer errors measuring left ventricular ejection fraction (3.7 vs. 10 avg.), LV end-diastolic volume (5.9 vs. 8.4 ML avg.), and LV mass (7.7 vs. 12g avg.).
- Sonosite LX: Fujifilm Sonosite launched its new flagship Sonosite LX “kiosk” ultrasound system, replacing the X-Porte and landing above the Sonosite PX. The Sonosite LX leads with its new 21.3” clinical display, which is the largest and highest-clarity display in its portfolio, adds adjustability features to accommodate more bedside settings (extends, rotates, tilts), and features an updated UI to support “heads-up” operation. Fujifilm Sonosite also launched the T8-3 transesophageal transducer and Cardiac Resuscitation exam (compatible w/ LX and PX systems) to support clinicians during ultrasound-informed resuscitation from cardiac arrest.
- Photon-Counting Coronary CTA: Radiology Journal published the first in-human study of photon-counting CTs’ performance for coronary CT angiography exams, while adding to PCCT’s growing list of advantages over traditional CT technology. The researchers performed coronary PCCT and energy-integrating detector dual-layer CT angiography exams on 14 patients and had three blinded radiologists evaluate the exams. The radiologists’ assigned the PCCT images higher scores for overall quality and diagnostic confidence (5 vs. 4 median for both, 1-5 scale), while PCCT images achieved significant improvements for diagnostic quality of calcification, stents, and noncalcified plaque (+100%, +92%, and +45% improvements).
- MIM Software & AMG Medtech’s British Isles Alliance: MIM Software and UK-based healthcare AI consultancy, AMG Medtech, announced that AMG Medtech will sell and market MIM Software’s medical imaging solutions in the UK and Ireland. MIM’s diverse list of imaging solutions (radiology, nuclear, cardiac, radiation oncology) seem to fit well with AMG’s portfolio, which includes both radiology (Arterys) and radiotherapy solutions (RADformation, IntraOp, Limbus AI, Proton, Sabr).
- Understanding Missed HNCs: A new CAR Journal study suggests that a meaningful number of head and neck cancers might have been detectable in previous imaging studies. The researchers reviewed 1,196 HNC patient cases, finding that the cancers were “clearly evident” in 46 patients’ previous CT and MRI studies (4%) but were either missed (32, 70%) or misinterpreted (14, 30%). To address this issue, the authors proposed increasing awareness of commonly missed HCN cancer locations and encouraging radiologists to review potential blind spots (e.g. nasopharynx or salivary glands in plain head CTs).
- NHS Breast Screening Shakeup: Mainstream media outlets in the UK recently ran stories suggesting that the NHS breast cancer screening program could be headed towards the “biggest shakeup” in its 30-year history. The articles detailed a range of ongoing breast cancer screening studies that could end up justifying younger screening ages (40yrs vs. 50yrs), new risk scoring tests (e.g., genetics, density), and risk-based screening plans (different exam frequency, modalities). However, the articles didn’t include any comments from the NHS and none of these studies are complete, so the “shakeup” that everyone is talking about could just be a more exciting way of covering ongoing screening studies.
- Probo’s New PE Parent: Private equity firm Avista Capital Partners acquired imaging parts/service/device company, Probo Medical, from its previous PE parent company (Varsity Healthcare) for an undisclosed sum. Probo joins Avista as a much different company than when Varsity acquired it in late 2018, following at least seven acquisitions that expanded Probo into new modalities, service lines, and geographies.
- Viz.ai ISC Evidence: Viz.ai was well represented at the AHA International Stroke Conference where its modules were featured in four studies. Viz.ai’s Viz LVO module (for large vessel occlusion) was highlighted in a UCSD paper showing a notable reduction in LVO “door to groin times” (n = 82; 50 to 39min overall) and in a Mount Sinai paper highlighting its detection rates (n = 1,822 CTAs; 100% w/ ICA terminus occlusions, 93% w/ M1 occlusions, 49% w/ M2 occlusions). Viz.ai’s Viz ICH module (for intracranial hemorrhage) was featured in an Ohio State study detailing its accuracy and ICH notification speeds (n = 611; 87.9% sensitivity, 98.3% specificity, 2.03min avg) and in a similar Mount Sinai accuracy study (n = 682, 89.3% sensitivity, 99.4% specificity, 99.5% NPV).
- Transparency Non-Compliance: A new survey of over 1k hospitals from PatientRightsAdvocate.org found that only 14% of hospitals currently comply with the federal cost of care transparency rule that took effect at the beginning of 2021. The most common act of noncompliance was lacking or incomplete posting of negotiated rates for service items from accepted health plans (including imaging), but it’s hard to predict that the situation will improve quickly given that the cost of compliance with the rule is $12k per hospital.
|
|
- See how Einstein Healthcare Network reduced its syringe expenses, enhanced its syringe loading, and improved its contrast documentation when it upgraded to Bayer Radiology’s MEDRAD Stellant FLEX CT Injection System.
- Associated Urologists of North Carolina just became the latest home of one of United Imaging’s uCT 530 CT systems. See why Associated Urologists’ Cary, NC office called United Imaging’s CT team “the best.”
- See how GE Healthcare’s CT lineup is helping radiologists and technologists become more efficient through effortless workflow, new AI efficiencies, and a unique approach to scanner modularity.
- Do you have the tools and knowledge to successfully navigate MACRA? See how Change Healthcare’s Quality Reporting Solution can help you succeed with MIPS without disrupting your workflow.
- In this Fujifilm Healthcare post, VidiStar users share how they’ve benefitted from the cardiovascular information system’s flexible SaaS-based model and leveraged its productivity advantages to increase reimbursements.
|
|
|
|
|