|
AI Disparity Detection | MaxQ Pivot
January 17, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“I’ve never heard of digital colonoscopies, but as you can tell from my age, I could use a couple.”
|
|
Jon Stewart after Mark Cuban told him (and many thousands of viewers) about the cost and comfort benefits of virtual CT colonoscopies.
|
|
|
|
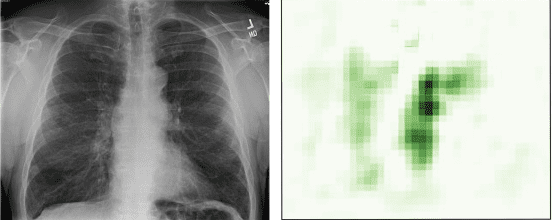
Most studies involving imaging AI and patient race/ethnicity warn that AI might exacerbate healthcare inequalities, but a new JACR study outlines one way that imaging AI could actually improve care for typically underserved patients.
The AI vs. EHR Disparity Problem – The researchers used a deep learning model to detect atherosclerotic disease in CXRs from two cohorts of COVID-positive patients: 814 patients from a suburban ambulatory center (largely White, higher-income) and 485 patients admitted at an inner-city hospital (largely minority, lower-income).
When they validated the AI predictions versus the patients’ EHR codes they found that:
- The AI predictions were far more likely to match the suburban patients’ EHR codes than the inner-city patients’ EHR codes (0.85 vs. 0.69 AUCs)
- AI/EHR discrepancies were far more common among patients who were Black or Hispanic, prefer a non-English language, and live in disadvantaged zip codes
The Imaging AI Solution – This study suggests healthcare systems could use imaging AI-based biomarkers and EHR data to flag patients that might have undiagnosed conditions, allowing them to get these patients into care and identify/address larger systemic barriers.
The Value-Based Care Justification – In addition to healthcare ethics reasons, the authors noted that imaging/EHR discrepancy detection could become increasingly financially important as we transition to more value-based models. AI/EHR analytics like this could be used to ensure at-risk patients are cared for as early as possible, healthcare disparities are addressed, and value-based metrics are achieved.
The Takeaway – Over the last year we’ve seen population health incidental detection emerge as one of the most exciting imaging AI use cases, while racial/demographic bias emerged as one of imaging AI’s most troubling challenges. This study managed to combine these two topics to potentially create a new way to address barriers to care, while giving health systems another tool to ensure they’re delivering value-based care.
|




|
|
No blueprint? No problem.
Live Site Planning Sessions are one of United Imaging’s favorite collaboration moments, giving customers and their design team an opportunity to discuss preliminary equipment layout, adjust equipment placement, make changes to the floor plan, and review equipment specifications in a live virtual environment.
|
|
Einstein & Bayer’s Injection System Upgrade
See how Einstein Healthcare Network reduced its syringe expenses, enhanced its syringe loading, and improved its contrast documentation when it upgraded to Bayer Radiology’s MEDRAD Stellant FLEX CT Injection System.
|
|
- MaxQ Pivot: Aunt Minnie revealed that MaxQ AI’s move to shut down its Accipio commercial operations was part of the company’s pivot outside of imaging. MaxQ will now develop AI algorithms that health systems would use to analyze their medical data and “identify anomalies that may cause poor clinical outcomes or care inefficiencies.” These new details don’t bring many tangible changes within radiology (Accipio is still shut down, MaxQ is still out of imaging), but the fact that MaxQ decided to cancel its only product and refocus its AI engineers / IP outside of imaging carries some symbolic significance.
- AB-MRI Beats DBT: A new Academic Radiology study revealed that abbreviated breast MRI (AB-MRI) might be far more effective than DBT for screening women with a history of breast cancer (n = 471, 54.5yr avg age). AB-MRI detected all of the participants’ cancer recurrences (11 vs. DBT’s 6), while achieving a far higher cancer detection rate (23.4 vs. 12.7 per 1k), sensitivity (100% vs. 54.6%), and AUC (0.983 vs. 0.761), with only slightly lower specificity (96.5% vs. 97.6%).
- Medically Home’s $110M: Hospital-at-home company Medically Home completed a new $110M funding round (total now $275M) that it will use to expand its capabilities and geographic reach. In a sign of healthcare insiders’ bullish expectations for at-home care (and potentially at-home imaging), Medically Home’s main investors include Cardinal Health, Mayo Clinic, Kaiser Permanente, Baxter International, and Global Medical Response.
- Patient Portal Non-Impact: The expanded role of medical image viewing through online patient portals hasn’t had much of an impact on most radiologists. A Journal of Digital Imaging study of three healthcare systems and 254 of their radiologists found that patients viewed 14% of available exams and only 36% of the radiologists were ever contacted by patients about their online images (of them 46.5% were contacted 1-2 times/yr, 46.5% 3-4 times/yr). The majority didn’t feel online viewing impacted their roles as radiologists (76%), although 11.8% felt a negative impact and 9.3% saw portal viewing positively.
- BoneMRI FDA: MRIguidance’s BoneMRI image processing software now has FDA clearance for pelvic imaging, representing a key milestone for the Dutch startup and for its unique software that transforms MRI images into CT-quality 3D bone scans. MRIguidance expects to add FDA clearances for cervical and lumbar spine exams later this year, matching BoneMRI’s CE Markings.
- 2021’s Record Funding: A new Rock Health report revealed that US digital health startups brought in a whopping $29.1B in investments last year across 729 deals, nearly doubling 2020’s former record of $14.9B (440 deals). Although a relatively small portion of 2021’s funding went to imaging startups, three of the six most-funded clinical indications were imaging related: cardiovascular ($1.8B, #3), MSK ($1.4B, #5), and oncology ($1.4B, #6).
- MIT’s AI Screening Guidelines: The MIT-led team that developed the Mirai breast cancer risk model unveiled their new “Tempo” AI-based personalized screening framework (determines personal screening cadences), suggesting that pairing the two systems could improve early detection while reducing over-screening. Tempo uses Mirai-based risk assessments to produce personalized follow-up plans, and in a validation across four hospitals led to more early breast cancer detections per screening compared to following the current guidelines.
- Touchstone Incident: Large imaging center company Touchstone Medical Imaging shut down its Dallas-area imaging operations in late December after a “security incident.” Touchstone hasn’t provided details on the incident or what patient data might be exposed, but they have since resumed services. If this sounds familiar, the US Radiology subsidiary was previously fined $3M for a 2014 breach that exposed over 300,000 patients’ health information.
- AI-LAVi with LDCTs: A MUSC-led team developed a deep learning algorithm that can automatically measure and segment left atrial volumes (LAVs) using LDCT lung cancer screening exams, showing that these AI results could be used to predict cardiac health. The “AI-LAVi” algorithm and three expert cardiothoracic radiologists quantified left atrial volumes in 273 LDCT exams, achieving “excellent correlation.” AI-LAVi also showed promise for predicting new-onset atrial fibrillation (AUC 0.86, OR 1.12), heart failure hospitalization (AUC 0.90, OR 1.07), and major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (AUC 0.68, OR 1.04) within 5 years.
- Xvision Looks West: Romanian AI startup Xvision just landed a €1M Seed round that it will use to expand its team and fund its expansion into Western Europe and the US. Xvision’s AI tools for CXR and chest CT analysis are already in use at over 60 hospitals in Central and Eastern Europe and have been found to cut radiologist interpretation times by 25% to 30%.
- Hospital Performance: November’s hospital performance data from Kaufman Hall showed operating margins up 8.1% from October, while still down 22.1% compared to pre-pandemic levels due to ongoing labor shortages and supply chain issues. While the report shows what could be considered a recovery in hospital performance, November’s data is largely prior to the recent surge in omicron cases, and worse results are expected in December.
|
|
Creating Your AI Platform Strategy
Adopting a platform strategy can simplify the deployment and management of imaging applications and AI algorithms, but there’s a lot to consider. In this eBook, Blackford Analysis and its clients detail how AI platforms can benefit clinical and IT teams, and share guidelines to consider when selecting a platform.
|
|
- See how Florida’s Medical Center Radiology Group (MCRG) improved its workload distribution, team communication, and overall productivity after implementing Nuance’s PowerScribe Workflow Orchestration and PowerConnect Communicator solutions.
- When the demand for your PET/CT imaging services outpaces available appointments, what are your options? Learn how Hackensack University Medical Center optimized its clinical operations by upgrading its Biograph Horizon to TrueV technology in this new case study from Siemens Healthineers.
- Do your patients text more than they use CDs? Find out how Novarad’s CryptoChart simplifies image access, combining secure QR codes and text and email communications to help providers and patients ditch the disk.
- Watch CriticalCare’s Dr. Yusuf Karrar, MD discuss how Canon’s CT Fluoro touch interface allows “Simple, Streamlined CT Fluoroscopy.”
- Check out this Imaging Wire Show interview with Riverain Technology’s Chief Science Officer, Jason Knapp, where we discuss the evolution of imaging AI, how to get generalizability right, AI’s path forward, and much more.
- This University of Chicago study detailed an Arterys-based non-contrast 4D-flow CMRI sequence that acquires multiple overlapping thin slabs, and could improve image quality, diagnostic accuracy, and aortic flow measurements compared to the non-contrast single-slab approach.
- Check out this Imaging Wire Show, featuring Nanox AI strategy leader, Dr. Orit Wimpfheimer, where we discuss building an international telerad practice, what’s wrong with triage AI, and pivoting to population health AI.
- Rising CT volumes and related costs are creating new pressures on CT teams, but these trends can be corrected through greater communication, education, and awareness. See how in this new GE Healthcare report.
|
|
|
|
|