|
Trained to Underdiagnose | Nationwide Imaging
December 16, 2021
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“For the number of people that read their own scans and don’t find radiology helpful/don’t use the reports, we sure get A LOT of phone calls in a day.”
|
|
A particularly popular tweet from Dr. Shadowgazer.
|
|
|
|
A new Nature study suggests that imaging AI models might underdiagnose patient populations who are also underdiagnosed in the real world, revealing new ethical and clinical challenges for AI development, regulation, and adoption.
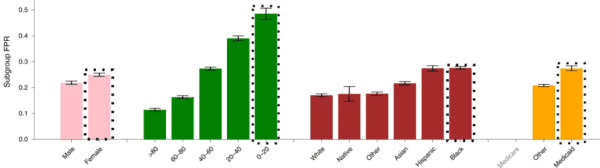
The Study – The researchers trained four AI models to predict whether images would have positive diagnostic findings using three large/diverse public CXR datasets (one model w/ each dataset, one w/ combined dataset, 707k total images). They then analyzed model performance across various patient populations.
The Underdiagnosed – The AI models were mostly likely to underdiagnose patients who are female, young (0-20yrs), Hispanic and Black, and covered by Medicaid (low-income). AI underdiagnosis rates were even more extreme among patients who belonged to multiple underserved groups, such as Hispanic females or younger Black patients.
The Overdiagnosed – As you might expect, healthy patients who were incorrectly flagged by the AI models as unhealthy were usually male, older, White, and higher income.
The Clinical Impact – In clinical use, a model like this would result in traditionally underserved patients experiencing more missed diagnoses and delayed treatments, while traditionally advantaged patients might undergo more unnecessary tests and treatments. And we know from previous research that AI can independently detect patient race in scans (even if we don’t know why).
The Takeaway – AI developers have been working to reduce racial/social bias in their models by using diverse datasets, but it appears that they could be introducing more systemic biases in the process (or even amplifying them). These biases certainly aren’t AI developers’ fault, but they still add to the list of data source problems that developers will have to solve.
|




|
|
Siemens’ Photon-Counting CT Impact
How could photon-counting CT impact your patients? In this video, the Medical University of South Carolina, one of the first users of the NAEOTOM Alpha, talks about the potential to visualize small lesions and fine details for high diagnostic confidence in neurology, cardiology, oncology, and pulmonology.
|
|
- DispatchHealth’s Nationwide Imaging: Home care giant DispatchHealth just became one of the US’ largest mobile imaging providers with its acquisition of Dynamic Mobile Imaging. The acquisition expands DispatchHealth’s imaging services across much of the Midwest and Eastern US, and comes about eight months after first entering the imaging segment through its acquisition of Professional Portable X-Ray. Mobile imaging plays a key role in DispatchHealth’s strategy to create the “world’s largest in-home care system,” suggesting that more regional imaging acquisitions might be on the way.
- Advanced-EPI’s Pancreatic Advantage: A new study out of Germany detailed an optimized MRI diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) sequence with advanced imaging post-processing / motion correction (advanced-EPI) that outperforms standard DWI (standard-EPI) for pancreatic imaging. Two blinded radiologists reviewed 62 patients’ abdominal 1.5T MRIs with advanced-EPI and standard-EPI, finding that advanced-EPI was preferred in 96% of cases and yielded “significantly higher” scores across a range of pancreatic imaging parameters (e.g. image quality, parenchyma details, sharpness of boundaries).
- Philips’ Echo Experience: Philips announced what it’s calling a “fully integrated echocardiography experience,” combining its EPIQ CVx and Affiniti CVx ultrasound platforms with a new X5-1c transthoracic transducer, AI-driven automated measurement apps, and remote tele-ultrasound diagnostic access.
- The Adversarial AI Threat: A new University of Pittsburgh study revealed that artificially-created “adversarial images” can fool both AI detection systems and subspecialist radiologists, highlighting a potential AI safety vulnerability. The researchers intentionally modified the diagnosis-sensitive areas of mammogram images, fooling an AI-CAD tool into producing a wrong diagnosis with 69% of images (all were diagnosed correctly pre-modification). Radiologists might not be able to serve as a safety net, as five breast rads were only able to visually identify 29% to 71% of the altered adversarial images.
- Guerbet & Bracco’s GBCA Alliance: Guerbet and Bracco Imaging announced plans to collaborate on the manufacturing, R&D, and regulatory clearance of their next-gen Gadopiclenol MRI agent, while independently commercializing it under separate brands as early as 2023. Both companies own intellectual property related to Gadopiclenol, although Guerbet developed it and will manufacture Gadopiclenol’s active ingredient and vials for Bracco for up to seven years.
- FFR-CT Effectiveness: FFR-CT has been one of imaging AI’s success stories, but a new study in European Radiology suggests that it might be less effective for evaluating the distal coronary artery segment. The researchers analyzed FFR-CTs from 59 asymptomatic male marathon runners without coronary artery stenosis (in proximal, mid, and distal coronary sections), finding that 22 of the participants (37%) had abnormal distal FFR-CT values (≤ 0.8) even though they were healthy. Although the study was performed using a prototype on-site FFR-CT system (not HeartFlow), it prompted an interesting debate about FFR-CT’s actual capabilities.
- Mammography Self-Scheduling Benefits: A new Mayo Clinic study highlighted their mammography screening self-scheduling platform’s impact on patient convenience and staff workloads. Fifteen percent of patients used the scheduling platform in its first year (14k/93k), with 75% of self-scheduling happening during non-business hours. The self-scheduled appointments were far more likely to require a single setup step than staff-scheduled visits (93.5% vs. 74.5%) and rarely required staff to “clean up” incorrect appointment settings, although they also had higher no-show rates (5.7% vs. 4.6%).
- Sonic Incytes’ Launch Funding: Sonic Incytes completed a $7.3M Series A round (total now $10.6M) and announced the launch of its Velacur handheld 3D ultrasound solution, which assesses fatty liver disease in 5-minutes with accuracy that’s “comparable to” MRI elastography. The FDA-cleared solution combines a handheld ultrasound that is placed between a patient’s ribs with an activation pad positioned underneath the patient, creating steady waves to quantify liver steatosis (fat content) and stage fibrosis (tissue stiffness).
- Pediatric Pneumonia Predictor: A new Pediatrics Journal study detailed a predictive model that uses clinical data to identify children with and without community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), helping to guide chest X-ray and antibiotic use decisions. The researchers analyzed 1,142 patients (3mo – 18yrs, 253 w/ CAP) with signs of lower respiratory infection, finding that a model based on age, fever duration, tachypnea, and focal decreased breath sounds had “excellent” performance identifying patients with and without CAP.
- Feedback & AWS’ TB Solution: Feedback PLC announced that it received funding from Amazon Web Services to support its rural India cloud-based tuberculosis (TB) screening program. The AWS-hosted solution allows local clinicians to upload chest X-rays to Feedback’s Bleepa app, which would then share images for diagnosis (either w/ remote radiologists or AI tools) and support patient-specific communications between remote TB specialists and local screening personnel. All resulting images, reports, and clinical discussions would be stored in Feedback’s CareLocker.
- RadNet’s Delaware Expansion: Imaging center giant RadNet will expand into southern Delaware following its Delaware Imaging Network subsidiary’s acquisition of Dover-based Mid-Delaware Imaging (one location, full modality list). The acquisition gives RadNet its ninth imaging center in Delaware and continues its aggressive M&A activity within its targeted states (CA, AZ, NY, NJ, DE, MD).
|
|
Novarad’s Simple & Secure Patient Engagement
Evaluating your patient engagement strategy? Check out this Imaging Wire Show featuring Novarad’s Paul Shumway for a great conversation about how new technologies are helping imaging providers safely and securely improve patient engagement.
|
|
- Considering your short and long-term AI plan? Check out Canon Medical’s recent State of AI Roundtable, sharing insights into how imaging AI is being used, where it’s needed most, and how AI might assume a core role in medical imaging.
- See how Fujifilm Healthcare VidiStar users have benefitted from the cardiovascular information system’s flexible SaaS-based model and leveraged its productivity advantages to increase reimbursements.
- Discover how Magnolia Regional Health Center started catching more cancers sooner using Nuance’s PowerScribe Lung Cancer Screening Program and PowerScribe Follow-up Manager.
- Working on your organization’s AI strategy? This Blackford Analysis post outlines the key considerations for creating your AI goals and strategy, including some you might not have considered.
- United Imaging’s uMR OMEGA MR has been recognized in Fast Company’s 2021 Innovation by Design Awards. It launched with a 75 cm bore, which is the world’s largest high-field MR, making it more accommodating for those with broader body types, children, older patients, pregnant women, and people with claustrophobia.
- Ready to act today in order to thrive tomorrow? This GE Healthcare report details the three steps that healthcare institutions can take to improve productivity, effectiveness, efficiency, and patient outcomes.
|
|
|
|
|